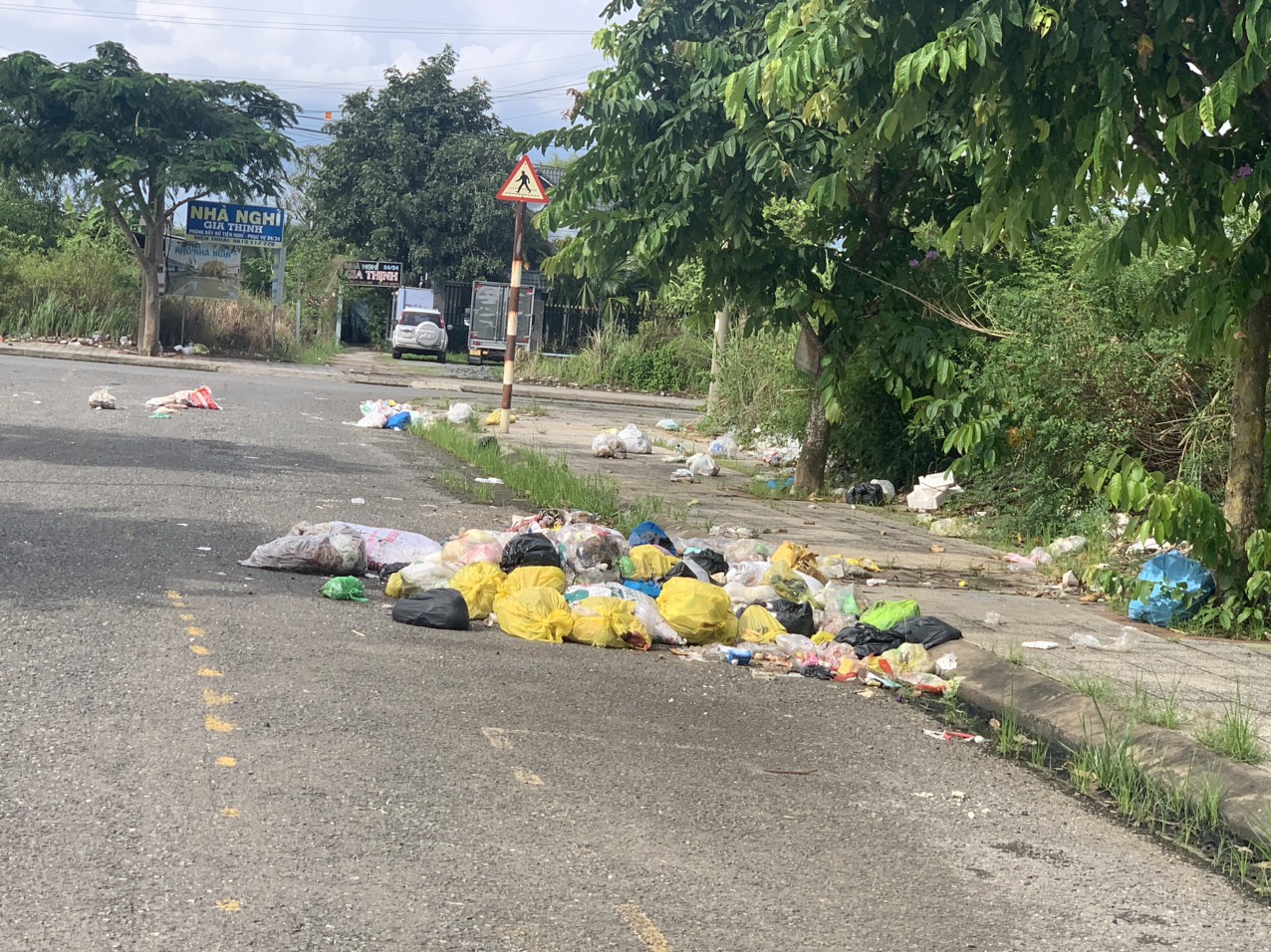
Trân trọng giới thiệu tới quý độc giả Công bố quốc tế lĩnh vực môi trường số 38-2023 với những nội dung chính như sau:
Về quản lý môi trường
– Mối liên hệ giữa môi trường xây dựng, hành vi đi lại và sức khỏe con người: Một khuôn khổ tích hợp để cải tiến hệ thống giao thông.
– Làm sáng tỏ hiệu quả của đổi mới xanh và thuế trong việc thúc đẩy chất lượng môi trường: Đánh giá mô hình kép để kiểm tra lý thuyết LCC ở các nền kinh tế mới nổi.
– Hiệu suất sử dụng than, sự không chắc chắn về chính sách khí hậu và tiêu thụ năng lượng xanh có thúc đẩy sự bền vững môi trường ở Hoa Kỳ không? Một ứng dụng của các công cụ Wavelet mới.
– Hiệu quả môi trường của đầu tư nghiên cứu và phát triển năng lượng sạch: Bằng chứng từ Nhật Bản bằng cách sử dụng hệ số công suất tải.
– Đánh giá vòng đời hệ thống quản lý rác thải điện tử tại Australia: Trường hợp bảng mạch in (PCB) thải.
– Hướng tới vận tải hành khách bền vững: Các kịch bản giảm phát thải carbon cho một thành phố cỡ trung bình.
– Từ rác thải thành hóa chất: Giải pháp xanh cho thị trường kinh tế sinh học.
– Chất hấp phụ xốp được điều chế từ các mẫu bọt nước thân thiện với môi trường và được cacbon hóa để xử lý đất.
– Liên kết năng lực môi trường nội bộ với lợi thế cạnh tranh bền vững trong các doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ trong lĩnh vực sản xuất: Vai trò trung gian của đổi mới sinh thái.
Về môi trường đô thị
– Làm thế nào có thể quy hoạch không gian xanh đô thị để giảm thiểu hiệu ứng đảo nhiệt đô thị trong các bối cảnh khí hậu khác nhau?
– Chì trong nước uống tổng hợp và nước uống đô thị thay đổi tùy theo thực địa so với phân tích trong phòng thí nghiệm.
– Tính khả thi về mặt kinh tế của việc đạt được tòa nhà phát thải ròng bằng không (NZEB) bằng cách áp dụng các nguồn năng lượng mặt trời và địa nhiệt vào hệ thống bơm nhiệt: Một trường hợp trong khu dân cư Hoa Kỳ.
– Những hiểu biết mới về cấu trúc và chức năng của bãi rác nhựa chất thải rắn đô thị (MSW).
– PFAS trong nước rỉ rác bãi rác đô thị: Sự xuất hiện, sự biến đổi và nguồn.
– Một cách tiếp cận tổng hợp để kiểm tra sự phân mảnh đô thị ở các khu vực đô thị: Ý nghĩa đối với quy hoạch đô thị bền vững.
– Đôi bên cùng có lợi cho môi trường và kinh tế: Phân tích tối đa hóa lợi ích trong các nhà máy xử lý bùn thải đô thị.
– Các kỹ thuật quản lý chất thải rắn được hỗ trợ bởi các phương pháp tiếp cận in-silico với trọng tâm đặc biệt là quản lý chất thải rắn đô thị: Xu hướng và thách thức nghiên cứu.
– Các hợp chất lưu huỳnh hữu cơ trong vật chất hạt mịn xung quanh ở khu vực thành thị: Những phát hiện về phương pháp tiếp cận không nhắm mục tiêu.
Về môi trường khu công nghiệp
– Phương pháp thiết kế nhiều giai đoạn cho hệ thống điện và hơi nước kết hợp năng lượng nhiệt mặt trời và thu hồi nhiệt thải trong nhà máy lọc dầu.
– Giảm thiểu chi phí điện năng đa mục tiêu và giảm thiểu lượng khí thải CO2 gián tiếp trong các tòa nhà thương mại và công nghiệp sử dụng hệ thống lưu trữ năng lượng pin độc lập.
– Phát thải carbon và khử cacbon: Vai trò và sự liên quan của ngành lên men trong lĩnh vực hóa chất.
– Liên kết năng lực môi trường nội bộ với lợi thế cạnh tranh bền vững trong các doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ trong lĩnh vực sản xuất: Vai trò trung gian của đổi mới sinh thái.
– Thảm họa môi trường liên quan đến khai thác mỏ: Quan điểm của Tổ chức có độ tin cậy cao (HRO).
– Tổng quan về công nghệ xử lý đầu cuối CO trong ngành thép.
– Thiết lập hệ thống năng lượng cộng đồng công nghiệp: Mô phỏng vai trò của thiết kế thể chế và các thuộc tính xã hội.
– Phân hủy quang cực nhanh của thuốc nhuộm công nghiệp dệt bằng cách sử dụng vật liệu nanocompozit bậc ba dựa trên sunfua hiệu quả.
– Chiến lược và đặc điểm phát triển công nghiệp sinh thái theo đánh giá hiệu quả hoạt động của các dự án khu công nghiệp sinh thái ở Hàn Quốc.
– Ý nghĩa của Công nghiệp 5.0 đối với sản xuất bền vững toàn diện: Lộ trình chiến lược dựa trên kiến thức bằng chứng.
– Thuế môi trường dưới sự độc quyền hỗn hợp: Vai trò của tư nhân hóa và công nghệ sinh thái nước ngoài.
– Giảm tác động môi trường của việc sản xuất thịt gà Brazil bằng các chiến lược thu hồi chất thải khác nhau.
CHUYÊN TRANG QUẢN LÝ MÔI TRƯỜNG
Tạp chí Môi trường và Đô thị Việt Nam
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!
QUẢN LÝ MÔI TRƯỜNG
1. How does internet development drive the sustainable economic growth of China? Evidence from internal-structural perspective of green total-factor productivity
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 887, 20 August 2023, 164125
Abstract
Clarifying internal-structural transmission paths of internet development on China’s green total-factor productivity (GTFP) is of great significance for understanding China’s economic growth in the era of digital transition. In this paper, GTFP is decomposed by three-hierarchy meta-frontier DEA into technology, industrial structural, regional balance development, scale, and management efficiencies based on China’s provincial data. Then, dynamic GMM models are applied to investigate the internal-structural effect of internet development on GTFP. The results illustrate that internet development significantly improves GTFP by promoting technology, optimizing industrial structural, and advancing scale efficiencies. But it inhibits regional balance development and management efficiencies. Based on the results, this study offers new insights and valuable policy implications for China to promote sustainable economic growth.
2. Nexus between built environment, travel behaviour and human health: An integrated framework to reinform transport system
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137744
Abstract
Transport systems play a significant role in socio-economic development and influence a city’s human health (HH) status mediated through multiple pathways. It fosters the growth trajectory of a city by acting as its lifeline. However, many factors like a city’s-built environment (BE), travel behaviour (TB), travel patterns and socioeconomic status of urban commuters influence the transport system. A vast amount of literature is available in silos that evaluates the relationship between any two components, especially in the context of developed countries. So far, the research community has not agreed on the underlying nexus between BE, TB, and human health (HH). Given this, the present study aims to (i) assess the relationship (both intensity and magnitude) between BE, TB and HH; (ii) summarise the statistical tools used to assess these relationships, (iii) critically analyse existing studies and develop a conceptual model of BE-TB-HH (BETH) nexus and (iv) conduct logical framework analysis to identify linkages between BETH nexus and sustainable development goals (SDGs). Study results suggest that the BETH nexus is multidimensional, complex and dynamic, which operates at different spatial scales and can help achieve a country’s nationally determined commitments and SDGs. BETH nexus integrates management and governance across multiple sectors of urban planning, transportation, individual psychology, and human health. It corroborates the need not to view urban planning, transportation, human health, and human psychology as separate entities but as a complex and inextricably interlinked system framework that will help policy and decision-makers reinform the transport system.
3. Unravelling the efficacy of green innovation and taxation in promoting environmental quality: A dual-model assessment of testing the LCC theory in emerging economies
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137850
Abstract
The increasing impact of anthropogenic activities on the environment has led researchers to conduct a comprehensive analysis of its determinants and propose sustainable solutions to mitigate the negative effects. Given the situation, the load capacity factor (biocapacity/ecological footprint) is used in this study as a comprehensive indicator of environmental sustainability that takes into account the supply-side consequences of ecological concerns while evaluating the theoretical dynamics of the Load capacity curve (LCC) in emerging countries. In doing so, the study employed the novel Method of Moment Quantile Regression (MMQR) to analyze the role of green innovation, green taxation, and economic growth under the LCC framework, from 2000 to 2018. The results affirm the presence of a U-shaped curve between environmental sustainability and income implying that growth may cause to harm the environment but after reaching a certain turning point it maintains the ecological quality. Also, green measures of taxation and innovation could curb carbon dioxide emissions at various quantiles for the selected bloc of countries. Noticeably, the LLC hypothesis is verified for both models establishing a positive association of determinants with load capacity factor. The results recommended policy implications for emerging countries seeking to promote sustainable economic growth while preserving the environment.
4. Do coal efficiency, climate policy uncertainty and green energy consumption promote environmental sustainability in the United States? An application of novel wavelet tools
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 137851
Abstract
In 2020, the United States produced 4.7 billion metric tons of CO2, making it the world’s second-largest polluter. To achieve the SDGs, the United States has committed to reducing net CO2 emissions by 50–52% from 2005 levels by 2030. Therefore, this study examines the co-movement between CO2 and coal efficiency, climate policy uncertainty, green energy, and green innovation using data from 1990 to 2020. To support policymakers in developing sustainable energy policies at various times, we used wavelet cohesion, wavelet correlation, wavelet coherence, and the novel causality in continuous wavelet transform to investigate these connections. The wavelet coherence and wavelet cohesion results revealed that coal efficiency contributes to reducing CO2 emissions at different frequencies and times, while climate policy uncertainty reduces CO2 emissions in the long term. Moreover, green energy consumption and green innovation improve ecological quality by reducing CO2 in the short and medium term. Furthermore, wavelet causality analysis revealed that all indicators could predict CO2 emissions at different frequencies and time periods. Based on the overall findings of this research, we recommend that policymakers in the United States support green energy and energy efficiency initiatives as the most effective ways to reduce CO2 and address other critical climate issues.
5. Does financial stability inspire environmental innovation? Empirical insights from China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137896
Abstract
Environment-related innovations are widely appreciated as a vital factor in achieving sustainable development goals, and stability in the financial sector can help boost the output of environmental innovations by removing financial constraints. Hence, the primary aim of the analysis is to investigate the impact of financial stability on environmental innovation in China by using the QARDL model over the period 1995Q1-2020Q4. The study’s main findings confirm the positive role of financial stability on environmental innovation in both the short and long run. Wald test also confirms the asymmetric impact of financial stability on environmental innovation in the short and long run. Moreover, the long-run impacts of GDP, R&D activities, and environmental policy stringency on environmental innovation are positive. In the short run, the estimates of research and development and environmental policy stringency are positively significant at higher quantiles only. Based on the findings, our research will help policymakers to develop valuable policies for financial stability to enhance environmental innovation.
6. Tackling China’s local environmental policy implementation gap: An evolutionary game analysis of China’s environmental protection inspection system
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137942
Abstract
Despite China’s stringent environmental regulations, there has been a persistent policy implementation gap at local level, specifically due to local protectionism and inadequate enforcement measures. To address this issue, the Central Environmental Protection Inspection (CEPI) initiative was launched in 2016, replacing the Regional Environmental Protection Inspection (REPI) system. This study examines why the REPI failed to tackle the implementation gap and how the CEPI works. This is achieved by constructing a tripartite evolutionary game (EG) model consisting of the central government, local governments, and polluting enterprises. Using system dynamics (SD), the study simulates and analyzes the behavior and strategies of the three game players in two scenarios, namely weak and strong negative incentives. Then, this study analyzes the evolutionary process of environmental protection inspection (EPI) by means of a case study. The results show that: (1) the strategy adopted by polluting enterprises depends on the actual signal conveyed by the local governments. In addition, whether the strong regulatory signal of the central government can be effectively transmitted to polluting enterprises mainly depends on the attitude of the local governments. (2) The CEPI conveys a reliable commitment and provides effective external stimuli that adjust the incentive structure of local governments. Meanwhile, the REPI lacked significant punishment measures, which made it difficult for the central government’s environmental regulatory signals to reach polluting enterprises in an effective manner. This study contributes to a better understanding of the evolutionary process and causes of the EPI system, as well as how the Chinese government tackles the local environmental policy implementation gap.
7. What lies about circular economy practices and performance? Fresh insights from China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137893
Abstract
The circular economy has indeed been the subject of increasing academic and industry interest in recent years, particularly in the context of corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. This study explored the implications of circular economy practices for corporate performance using panel data from Chinese-listed firms between 2009 and 2019. To this end, the text analysis method was used to acquire the frequency of circular economy-related words to measure corporate circular economy practices. This study has yielded four main findings. First, circular economy practices can improve firm performance based on resource-based theory. Second, innovation and digital transformation strategies can amplify the positive impact, and resource use efficiency improvements are the principal means for circular economy practices. Third, there is firm heterogeneity in the influences of circular economy practices on corporate performance. Namely, the circular economy practices have a greater impact on state-owned enterprises, large enterprises, and heavily polluting enterprises. Fourth, only appropriate circular economy practices can positively impact firm performance. These findings suggest that circular economy practices are an effective model for sustainable corporate development. It is indeed important to understand the role of circular economy practices in emerging countries such as China, where rapid economic growth and urbanization have led to significant environmental challenges.
8. Environmental effect of clean energy research and development investments: Evidence from Japan by using load capacity factor
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137972
Abstract
In environmental economics, the load capacity factor has recently been empirically studied to demonstrate how human actions degrade the environment and how nature compensates for this damage. Therefore, the improvement of the load capacity factor by countries is a critical indicator for achieving Sustainable Development Goals. The study therefore examines the environmental effects of research and development investments in renewable and nuclear energy. In doing so, the study covers Japan; applies Fourier-based time series models (i.e., FMOLS as the base model and DOLS and CCR for the robustness); and uses data between 1974 and 2018. The estimation results present that (i) renewable energy research and development investments support the environment; (ii) economic growth and financial development degrade the environment; and (iii) nuclear energy research and development investments have no effect on the environment. Thus, the study recommends that Japan should contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals by concentrating its research and development investments on renewable energy sources instead of nuclear energy.
9. Life cycle assessment of e-waste management system in Australia: Case of waste printed circuit board (PCB)
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 418, 15 September 2023, 138082
Abstract
Electronic waste (e-waste) is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally. Recycling is one of the environment-friendly waste management strategies that creates a net environmental gain in recovering valuable materials. In some countries, downstream recycling (high-value material recovery) is done overseas, and Australia is one of them. Waste printed circuit board (PCB) is a critical component of various electronic equipment, and it contains metals such as copper, tin, gold, aluminium, iron, silver, and others. Waste PCB, as apart of e-waste is mainly recycled overseas in Australia. However, the overall environmental impacts of recycling the waste stream overseas have yet to be investigated. The benefits of recovering the material in Australia have yet to be extensively understood from a supply chain perspective. This study aims to develop multiple scenarios using lifecycle assessment (LCA) methodology to identify the best possible solution for waste PCB disposal (final sink) derived from e-waste. Using SimaPro and Ecoinvent databases, four scenarios have been developed, along with a baseline scenario where waste PCB is recycled overseas. Receipe 2016 impact assessment methodology was utilized for the analysis, and results of the study showed that Scenario 2 (integrated material and energy recovery) is the best approach for waste PCB recycling in Australia, while landfill and direct incineration were the identified two worst scenarios in terms of final disposal option. When choosing local recycling over overseas recycling of waste PCB (material recovery only), it was found that impact categories such as global warming (human health) and fossil resource scarcity were reduced by 53% and 98%, respectively. In addition, the net positive environmental gain could be achieved for human non-carcinogenic toxicity by 7.16% when the waste stream is recycled in Australia. Uncertainty analysis of the study showed that in almost all major impact categories, material and energy recovery together scored high compared to scenarios when only material recovery was considered. This study is the first systematic attempt to characterize system-level lifecycle environmental impact assessment for waste PCB recycling. Future policies and regulations should focus on data transparency and availability across the value chain, local infrastructure development, and resource circularity. This study will add value to decision-making, policy on investment and future policy planning. It will also help industry and researchers develop optimized recycling-focused low-emission resource recovery supply chains.
10. Towards sustainable passenger transport: Carbon emission reduction scenarios for a medium-sized city
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 418, 15 September 2023, 138149
Abstract
The sustainability of transportation systems is frequently linked to human preferences, hence it is pertinent to align quotidian commuting choices with sustainable development goals. The main goal of the present research was to simulate eight scenarios designed to reduce the carbon dioxide emissions of passenger transport in a Colombian medium-sized city, taking into account the Global Warming Potential (GWP) of public and private vehicles, obtained by means of Life-Cycle Assessment (LCA). In this work we compared the environmental efficiency of the scenarios in order to make a contribution to the scientific discussion on sustainable mobility policies. Measures such as reducing the number of the most polluting vehicles, optimising the modal shares of public and private transportation systems, integrating electric vehicles, increasing the use of bicycles, and reducing mobility, have been tested. The results show that the current annual emissions from passenger transport in the selected city (263.98 kt CO2-eq) could be decreased by up to 64.28% by implementing a 50% reduction in individual Trips per Day (TpD) and distances travelled by private and public vehicles. In addition, increasing the public bus fleet by 50% could yield a 56.92% reduction in the carbon dioxide released, while using an average occupancy of 30 passengers in buses could decrease the total emissions by 25.73%. Augmenting the occupancy ratio of private vehicles was shown to yield a 22.71% reduction in carbon dioxide released. Also, increasing the electric vehicle fleets by 50% can produce carbon emission reductions of 17.96% for the current energy mix and 20.08% for a 100% renewable energy mix; while boosting the use of bicycles and increasing the diesel car fleet yielded reductions of 9.24% and 5.06%, respectively. This article concludes that managing mobility and restricting commuting could be the most sustainable measure for life-cycle carbon emission reduction.
11. Does regional collaborative governance reduce air pollution? Quasi-experimental evidence from China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138283
Abstract
Regional collaborative governance has become one of the most significant trends in environmental protection due to its importance in suppressing pollution transfer. This paper employs panel data from 285 cities in China during 2003–2019 and a multi-period difference-in-differences (DID) method to evaluate the influence of regional collaborative governance on air pollution. Results show that regional collaborative governance significantly reduces air pollution. Heterogeneity assessment suggests that the inhibiting impact of regional collaborative governance on air pollution is long-term and increases temporally, whereas the spillover effect of regional collaborative governance is only significant in a specific range and decays spatially. In addition, the mechanism analysis reveals that regional collaborative governance reduces air pollution by increasing environmental regulation intensity, improving environmental governance efficiency, and promoting environmental protection technology. This study provides useful policy insights for policymakers seeking green and sustainable development to curb air pollution and improve environmental quality.
12. Association between long-term green space exposure and mortality in China: A difference-in-differences analysis of national data in 2000, 2010 and 2019
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 887, 20 August 2023, 164023
Abstract
Background
Effects of green space on human health have been well-documented in western, high-income countries. Evidence for similar effects in China is limited. Moreover, the underlying mechanisms linking green space and mortality are yet to be established. We therefore conducted a nation-wide study to assess the association between green space and mortality in China using a difference-in-difference approach, which applied a causal framework and well controlled unmeasured confounding. In addition, we explored whether air pollution and air temperature could mediate the association.
Methods
In this analysis, we collected data on all-cause mortality and sociodemographic characteristics for each county in China from the 2000 and 2010 censuses and the 2020 Statistical Yearbook. Green space exposure was assessed using county-level normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and the percentage of green space (forest, grasslands, shrub land and wetland). We applied a difference-in-differences approach to evaluate the association between green space and mortality. We also performed mediation analysis (by air pollution and air temperature).
Results
Our sample consisted of 2726 counties in 2000 and 2010 as well as 1432 counties in 2019. In the 2000 versus 2019 comparison, a 0.1 unit increase in NDVI was associated with a 2.4 % reduction in mortality [95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.4–4.3 %], and a 10 % increase in percentage of green space was associated with a 4.7 % reduction (95 % CI 0–9.2 %) in mortality. PM2.5 and air temperature mediated 0.3 % to 12.3 % of the associations.
Conclusions
Living in greener counties may be associated with lower risk of mortality in China. These findings could indicate the potential of a population-level intervention to reduce mortality in China, which has important public health implications at the county level.
13. Waste-to-chemicals: Green solutions for bioeconomy markets
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 887, 20 August 2023, 164006
Abstract
In the fast-developing time, the accumulation of waste materials is always in an uptrend due to population increases and industrialization. This excessive accumulation in waste materials harms the ecosystem and human beings by depleting water quality, air quality, and biodiversity. Further, by use of fossil fuel problem-related global warming, greenhouse gases are the major challenge in front of the world. Nowadays, scientists and researchers are more focused on recycling and utilizing different waste materials like a municipal solid waste (MSW), agro-industrial waste etc. The waste materials added to the environment are converted into valuable products or green chemicals using green chemistry principles. These fields are the production of energy, synthesis of biofertilizers and use in the textile industry to fulfil the need of the present world. Here we need more focus on the circular economy considering the value of products in the bioeconomic market. For this purpose, sustainable development of the circular bio-economy is the most promising alternative, which is possible by incorporating the latest techniques like microwave-based extraction, enzyme immobilization-based removal, bioreactor-based removal etc., for the valorization of food waste materials. Further, the conversion of organic waste into valuable products like biofertilizers and vermicomposting is also realised by using earthworms. The present review article focuses on the various types of waste materials (such as MSW, agricultural, industrial, household waste, etc.), waste management with current glitches and the expected solutions that have been discussed. Furthermore, we have highlighted their safe conversion into green chemicals and contribution to the bioeconomic market. The role of the circular economy is also discussed.
14. Can China achieve its 2030 and 2060 CO2 commitments? Scenario analysis based on the integration of LEAP model with LMDI decomposition
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 888, 25 August 2023, 164151
Abstract
China’s ambitious targets of peaking its Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions on or before 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality by 2060 have been a topic of discussion in the international community. This study innovatively combines the logarithmic mean Divisia index (LMDI) decomposition method and the long-range energy alternatives planning (LEAP) model to quantitatively evaluate the CO2 emissions from energy consumption in China from 2000 to 2060. Using the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) framework, the study designs five scenarios to explore the impact of different development pathways on energy consumption and related carbon emissions. The LEAP model scenarios are based on the result of LMDI decomposition, which identifies the key influencing factors on CO2 emissions. The empirical findings of this study demonstrate that the energy intensity effect is the primary factor of the 14.7 % reduction in CO2 emissions observed in China from 2000 to 2020. Conversely, the economic development level effect has been the driving factor behind the increase of 50.4 % in CO2 emissions. Additionally, the urbanization effect has contributed 24.7 % to the overall change in CO2 emissions during the same period. Furthermore, the study investigates potential future trajectories of CO2 emissions in China up to 2060, based on various scenarios. The results suggest that, under the SSP1 scenarios. China’s CO2 emissions would peak in 2023 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. However, under the SSP4 scenarios, emissions are expected to peak in 2028, and China would need to eliminate approximately 2000 Mt of additional CO2 emissions to reach carbon neutrality. In other scenarios, China is projected to be unable to meet the carbon peak and carbon neutrality goals. The conclusions drawn from this study offer valuable insights for potential policy adjustments to ensure that China could fulfill its commitment to peak carbon emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
15. Porous adsorbent prepared from eco-friendly aqueous foam templates and carbonized for soil remediation
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137757
Abstract
Porous adsorption materials have garnered extensive attention in environmental remediation in recent years, but green preparation and effective post-treatment remain the main challenges in practical applications. Here, a novel porous adsorbent was successfully fabricated from the aqueous foams templates stabilized by the natural plant Sapindus mukorossi (S. mukorossi) and nano-clay attapulgite (APT) via a thermally-initiated polymerization. The as-prepared porous adsorbents exhibited abundant interconnected pore structures and demonstrated excellent adsorption properties for chlortetracycline hydrochloride (CTC) and tetracycline hydrochloride (TC), with a maximum adsorption capacity of 620 mg/g and 538 mg/g, respectively. After adsorption, the waste porous adsorbent was converted into carbon/APT material through anaerobic calcination. At a carbonization temperature of 400 °C, carbon/APT with large amounts of negative charges and oxygen-containing functional groups exhibited a good adsorption capacity for Cd2+ and showed potential as a soil remediation agent. In summary, this study presents a feasible new idea for the green preparation and post-processing of waste adsorbents, offering a promising solution to the challenges faced in practical applications.
16. Linking internal environmental capabilities to sustainable competitive advantage in manufacturing SMEs: The mediating role of eco-innovation
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 137928
Abstract
With the world’s growing emphasis on environmental issues and the increased pressure on small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises (SMEs) to address such issues, sustaining competitiveness has become a critical concern for SMEs. Their organisational resources and capabilities must be configurated to align with environmental requirements to sustain their competitiveness. While mounting research has highlighted the importance of environmental capabilities in facilitating proactive environmental practices, it remains unclear how these capabilities can improve manufacturing SMEs’ sustainable competitive advantage (SCA). This study, therefore, has investigated how; green absorptive capacity, organisational capabilities and strategic environmental orientation have affected firms’ SCA, along with exploring the mediating effect of eco-innovation in such relationships. Using a sample of 176 manufacturing SMEs in Egypt, a cross-sectional survey approach was adopted to collect data on the research variables. The data were analysed using the Smart-PLS software application, and the results demonstrated the significant roles of; green absorptive capacity and strategic environmental orientation in facilitating eco-innovation, which in turn have helped SMEs sustain their competitive advantage. On the other hand, organisational capabilities did not appear to directly or indirectly affect firms’ SCA. Hence, this study may pique the interest of SME managers as it has emphasised the importance of strategic environmental orientation and green absorptive capacity in fostering eco-innovation and sustaining competitive advantage.
MÔI TRƯỜNG ĐÔ THỊ
1. How can urban green spaces be planned to mitigate urban heat island effect under different climatic backgrounds? A threshold-based perspective
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 890, 10 September 2023, 164422
Abstract
Urban green space (UGS) was widely regarded as an effective nature-based solution to mitigate the urban heat island (UHI) effect, therefore, developing landscape strategies to enhance its cooling intensity (CI) is crucial. However, two main problems prevent the application of results to practical actions: one is the inconsistency of relationships between influencing factors of landscape and the thermal environment; another is the unfeasibility of some common conclusions such as simply increasing the amount of vegetation cover in highly-urbanized areas. This study compared the CIs of UGSs, investigated the influencing factors of CI and identified the absolute threshold of cooling (ToCabs) of the influencing factors in four Chinese cities with very different climatic backgrounds (Hohhot, Beijing, Shanghai and Haikou). Results demonstrate that local climate condition affects the cooling effect of UGS. The CI of UGS is weaker in cities with humid and hot summer than in cities with dry and hot summer. Patch characteristics (area and shape), the percentage of water bodies within the UGS (Pland_w) and neighboring greenspace (NGP), vegetation abundance (NDVI) and planting structure together can explain a significant proportion (R2 = 0.403–0.672, p < 0.001) of the CI variations of UGS. The inclusion of water bodies can ensure effective cooling of UGS, except in the tropical city. Besides, ToCabs of area (Hohhot, 2.6 ha; Beijing, 5.9 ha; Shanghai, 4.0 and Haikou, 5.3 ha), and NGP (Hohhot, 8.5 %; Beijing, 21.6 %; and Shanghai, 23.5 %), NDVI (Hohhot, 0.31; Beijing, 0.33; and Shanghai, 0.39) were identified and related landscape strategies of cooling were proposed. The identification of ToCabs values can provide easy-to-use landscape recommendations to UHI mitigation.
2. Lead in synthetic and municipal drinking water varies by field versus laboratory analysis
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 891, 15 September 2023, 163873
Abstract
Water lead measurements by two field analyzers, relying on anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV) and fluorescence spectroscopy, were compared to reference laboratory measurements by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in progressively complex datasets (phases A, B, C), to assess field analyzer performance. Under controlled laboratory quantitative tests of dissolved lead within the field analysis range and optimal temperature range, lead recoveries by ASV ranged within 85–106 % of reference laboratory values (corresponding linear model: y = 0.96x, r2 = 0.99), compared to lower lead recoveries of 60–80 % by fluorescence (y = 0.69x, r2 = 0.99) in phase A. Field analyzer performance deteriorated in three opportunistic laboratory datasets compiled for phase B that contained dissolved lead (ASV: y = 0.80x, r2 = 0.98; no fluorescence data). Further lead underestimations were observed in five field datasets compiled for phase C, some of which contained known particulate lead (ASV: y = 0.54x, r2 = 0.76; fluorescence: y = 0.06x, r2 = 0.38). Deteriorating performance between phases was presumably due to the increasingly complex water matrices and lead particulates present in some phase C subsets (phase A < phase B < phase C). Phase C field samples had lead concentrations that were out-of-range, including a 5 % and 31 % false negative rate by ASV and by fluorescence, respectively. The range of results relevant to the diverse nature of compiled datasets, suggests that unless ideal conditions are known to be present (i.e., the lead content of water is dissolved within the field analysis range and optimal water temperature range), these field lead analyses might only be used as a water screening tool. Given the unknown conditions in many field settings, combined with the lead concentration underestimations including the false negative rates reported herein for field datasets, caution is encouraged when employing ASV and particularly fluorescence field analysis.
3. Biomonitoring trace metal contamination in Guangzhou urban parks using Asian tramp snails (Bradybaena similaris)
Chemosphere, Volume 334, September 2023, 138960
Abstract
Anthropogenic activities have caused environmental metal contamination in urban areas. Biomonitoring using organisms such as invertebrates can evaluate metal pollution, supplementing chemical monitoring, which cannot comprehensively reflect how metals influence organisms in the urban environment. To assess metal contamination in Guangzhou urban parks and its source, Asian tramp snails (Bradybaena similaris) were collected from ten parks in Guangzhou in 2021. The metal concentrations (Al, Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb, and Zn) were measured by ICP–AES and ICP–MS. We evaluated the metal distribution characteristics and correlations among metals. The probable sources of metals were determined by the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model. The metal pollution levels were analysed using the pollution index and the Nemerow comprehensive pollution index. The mean metal concentrations were ranked Al > Fe > Zn > Cu > Mn > Cd > Pb; metal pollution level in the snails was ranked Al > Mn > Cudouble bondFe > Cd > Zn > Pb. Pb–Zn–Al–Fe–Mn and Cd–Cu–Zn were positively correlated in all samples. Six major metal sources were identified: an Al–Fe factor corresponding to crustal rock and dust, an Al factor related to Al-containing products, a Pb factor indicative of traffic and industries, a Cu–Zn–Cd factor dominated by the electroplating industry and vehicle sources, an Mn factor reflecting fossil fuel combustion, and a Cd–Zn factor related to agricultural product use. The pollution evaluation suggested heavy Al pollution, moderate Mn pollution, and light Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb, and Zn pollution in the snails. Dafushan Forest Park was heavily polluted; Chentian Garden and Huadu Lake National Wetland Park were not widely contaminated. The results indicated that B. similaris snails can be used as effective biomarkers for monitoring and evaluating environmental metal pollution in megacity urban areas. The findings show that snail biomonitoring provides a valuable understanding of the migration and accumulation pathways of anthropogenic metal pollutants in soil‒plant–snail food chains.
4. The impact of urban agglomerations on carbon emissions in China: Spatial scope and mechanism
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138250
Abstract
Urban agglomerations have emerged as the dominant form of regional growth, but are also responsible for a vast majority of carbon emissions, making it a global concern. With China undergoing rapid construction of urban agglomerations, reducing carbon emissions is a significant challenge for its urbanization development. This study considers the construction of China’s urban agglomerations as a regional policy and utilizes the time-varying difference-in-differences method to investigate its impact on carbon emissions, as well as the effect’s spatial scope, mechanism, and heterogeneity. The findings reveal that 1) urban agglomerations can effectively reduce carbon emissions; 2) the optimal spatial scope for the reduction effect is within 50–100 km; 3) urban agglomerations can partially impact carbon emissions through the regional digital economy development level; and 4) the reduction effect varies based on the regional economic development level and green innovation capability. The study offers policy recommendations for the rational design of urban agglomerations’ spatial scope and the improvement of the digital economy level to achieve carbon emission reduction.
5. Economic feasibility of achieving net-zero emission building (NZEB) by applying solar and geothermal energy sources to heat pump systems: A case in the United States residential sector
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137822
Abstract
Buildings are one of the major sectors responsible for high energy demand and GHG emissions worldwide, which is driving expectations for implementing net-zero emission buildings (NZEBs) in many countries. Specifically, most developed countries have a carbon-neutral target set up for 2050, mandating all new buildings from then to be constructed as net-zero emission. Therefore, this paper investigated the economic feasibility of implementing NZEBs in the United States residential sector by combining a heat pump system with two renewable energy sources that are heavily supported by the federal government: solar and geothermal technologies. First, this study clearly demonstrates that “net-zero emission” is the most challenging task among neutralizing the energetic, economic, and environmental by-products from building operations. Moreover, this study analyzed the payback periods of multiple NZEB scenarios by considering the potential future changes in technology and policy necessarily required to meet the net-zero emission target by 2050. For reference, the technological and institutional factors were represented by “PV energy conversion rate” and “CO2 equivalent price of emission trading scheme (ETS)”, respectively. The results show that improving the PV energy conversion rate is much more effective in reducing the payback period of NZEBs compared to raising the CO2 equivalent price of ETS. However, the growing public awareness for this CO2 regulation policy will soon bring synergistic effect with the advancement of PV technology. In conclusion, this research framework clarifies the rather vague technological and institutional challenges that should be addressed to allow NZEBs to become economically feasible in the United States residential sector. Therefore, many building engineers, PV technicians, and policymakers should actively contribute to improving the techno-economic drivers for implementing NZEBs by 2050.
6. National water-saving city and its impact on agricultural total factor productivity: A case study of nine provinces along the Yellow River, China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 138019
Abstract
As an important water-saving regulation, the construction of national water-saving city (NWSC) plays an important role in agricultural production, however, there is little research on its impact on agriculture. This paper uses super efficient Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) to measure agricultural total factor productivity (ATFP) in the regions along the Yellow River, and uses difference-in-difference (DID) model to explore the impact of NWSC on ATFP based on the theory of production factor flow. The results show that: First, the ATFP in the regions along the Yellow River demonstrated an initial increase followed by a decrease from 2000 to 2019, the ATFP in the regions along the Yellow River is low in the north and high in the south, and the ATFP of the main grain producing areas is generally higher. Second, the establishment of the NWSC can effectively improve the ATFP, the ATFP has increased by 6.57% compared with the control group, and the dynamic effect of the policy has shown an “N” pattern since its implementation. Particularly, in areas with relatively poor water resources, high agricultural factor intensification and major grain production areas, NWSC has a stronger impact on the ATFP. Third, NWSC has promoted the flow of labor production factors and improved ATFP through income effect, industrial synergy effect and technological innovation effect. The transfer of agricultural labor has also injected strong impetus into industrial development, and improved the return on industrial capital, which can promote agricultural capital more significantly, and further improved ATFP. Our findings provide empirical evidence for achieving high-quality agricultural development through the construction of NWSC.
7. Coupled development of the urban water-energy-food nexus: A systematic analysis of two megacities in China’s Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138051
Abstract
Promoting the coupled development of water, energy, and food (WEF) subsystems is a critical step to enhance synergies and increase efficiencies in the WEF nexus. However, the evolution and obstacles of coupled development are largely ignored. This study developed a framework dividing links in the nexus to select indicators and integrated models for the degree of coordination and obstacle diagnosis to explore the coupled development of the WEF nexus from 2000 to 2020 in the water-scarce megacities of Beijing and Tianjin. The results show that the average coordination degree of the WEF nexus in Beijing (0.315) and Tianjin (0.317) is at a low level, indicating a limited interaction between the WEF subsystems, while the coordinated development degree of the WEF nexus is increasing. The order degree of the WEF subsystems shows a two-level hierarchical structure, indicating that both similarities and differences are included in place-specific characteristics. Furthermore, obstacle factors are identified from water and energy subsystems, in which environmental water use (W3) and the energy consumption per gross domestic production unit (E4) played the most significant roles and require a higher priority in policy response. The results in this paper complement obstacle factor analysis in WEF nexus practice, and provide operational indicators for nexus governance.
8. New insights on municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill plastisphere structure and function
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 888, 25 August 2023, 163823
Abstract
Plastisphere plays crucial role in global carbon and nitrogen cycles and microplastics formation. Global Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) landfills contain 42 % plastic waste, therefore representing one of the most significant plastispheres. MSW landfills are also the third largest anthropogenic methane sources and the important anthropogenic N2O source. Surprisingly, knowledge of microbiota and the associated microbial carbon and nitrogen cycles of landfill plastispheres is very limited. In this study, we characterized and compared the organic chemicals profile, bacterial community structure and metabolic pathway on plastisphere and the surrounding refuse in a large-scale landfill using GC/MS and 16S rRNA genes high-throughput sequencing, respectively. Landfill plastisphere and the surrounding refuse differed in organic chemicals composition. However, abundant phthalate-like chemicals were determined in both environments, implying the plastics additives leaching. Bacterial colonizing on the plastics surface had significantly higher richness than that in the surrounding refuse. Plastic surface and the surrounding refuse had distinct bacterial community composition. Genera of Sporosarcina, Oceanobacillus and Pelagibacterium were detected on the plastic surface with high abundance, while Ignatzschineria, Paenalcaligenes and Oblitimonas were rich in the surrounding refuse. Typical plastics biodegradation genus Bacillus, Pseudomonas and Paenibacillus were detected in both environments. However, Pseudomonas was dominant in plastic surface (up to 88.73 %), whereas Bacillus was rich in the surrounding refuse (up to 45.19 %). For the carbon and nitrogen cycle, plastisphere was predicted to had significant (P < 0.05) higher functional genes involved in carbon metabolism and nitrification, indicating more activated carbon and nitrogen microbial activity on the plastics surface. Additionally, pH was the main driver in shaping the bacterial community composition on plastic surface. These results indicate that landfill plastispheres serve as unique niches for microbial community habitation and function on microbial carbon and nitrogen cycles. These observations invite further study of the landfill plastispheres ecological effect.
9. PFAS in municipal landfill leachate: Occurrence, transformation, and sources
Chemosphere, Volume 334, September 2023, 138924
Abstract
To understand sources and processes affecting per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), 32 PFAS were measured in landfill leachate from 17 landfills across Washington State in both pre-and post-total oxidizable precursor (TOP) assay samples, using an analytical method that was the precursor to EPA Draft Method 1633. As in other studies, 5:3FTCA was the dominant PFAS in the leachate, suggesting that carpets, textiles, and food packaging were the main sources of PFAS. Total PFAS concentrations (Σ32PFAS) ranged from 61 to 172,976 ng/L and 580–36,122 ng/L in pre-TOP and post-TOP samples, respectively, suggesting that little or no uncharacterized precursors remained in landfill leachate. Furthermore, due to chain-shortening reactions, the TOP assay often resulted in a loss of overall PFAS mass. Positive matrix factorization (PMF) analysis of the combined pre- and post-TOP samples produced five factors that represent sources and processes. Factor 1 consisted primarily of 5:3FTCA (intermediate of 6:2 fluorotelomer degradation and characteristic of landfill leachate), while factor 2 was dominated by PFBS (degradant of C-4 sulfonamide chemistry) and, to a lesser extent, by several PFCAs and 5:3FTCA. Factor 3 consisted primarily of both short-chain PFCAs (end-products of 6:2 fluorotelomer degradation) and PFHxS (derived from C-6 sulfonamide chemistry), while the main component of factor 4 was PFOS (dominant in many environmental media but minor in landfill leachate, perhaps reflecting a production shift from longer to shorter chain PFAS). Factor 5, highly loaded with PFCAs, was dominant in post-TOP samples and therefore represented the oxidation of precursors. Overall, PMF analysis suggests that the TOP assay approximates some redox processes which occur in landfills, including chain-shortening reactions which yield biodegradable products.
10. Organosulfur compounds in ambient fine particulate matter in an urban region: Findings of a nontargeted approach
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 887, 20 August 2023, 164114
Abstract
Organosulfur compounds (OSCs) are important components of fine particulate matter (PM2.5); however, little information is available on OSCs in urban regions due to their chemical complexity, especially for novel species such as aromatic sulfonates. To supplement the detection technique and systematically identify OSCs, in this study we developed a nontargeted approach based on gas chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry (GC-HRMS) to screen OSCs in PM2.5 of urban Beijing and provide field evidence for their source and formation mechanism. 76 OSCs were found through mass difference of sulfur isotopes and characteristic sulfur-containing fragments. 6 species were confirmed as aromatic sulfonates by authentic standards. 32 OSCs showed higher levels in the heating season, presumably because of the intensive emission, especially from coal combustion. While certain species, with 2-sulfobenzoic acid as the representative, were 2.6-times higher in the non-heating season than in the heating season. Such species were significantly correlated with ozone and aerosol liquid water content (r = 0.2–0.8, p < 0.05), implying an oxidation-involved aqueous-phase formation in the atmosphere. In addition, with an average proportion of ∼95 % of the total sulfobenzoic acids, the predominance of the 2-substitution product over its isomers of 3- or 4-sulfobenzoic acid suggests a more plausible mechanism of radical-initiated reaction of phthalic acid followed by sulfonation, with atmospheric reactivity indicated by ozone and temperature as the determining factor. This study provided not only a nontargeted approach for OSCs in ambient PM2.5, but also field evidence on their secondary formation proposed in previous simulation studies.
11. An integrated approach for examining urban fragmentation in metropolitan areas: Implications for sustainable urban planning
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138151
Abstract
Urban fragmentation is generally regarded as a strong urban structural polarisation that is closely related to sustainability, yet a comprehensive understanding of the management of different fragmentation scenarios and their causes is still lacking. The Wuhan metropolitan area, as a rapidly urbanising region, shows clear evidence of different forms of urban fragmentation due to rapid urbanisation and spatial differentiation in pedestrian network structure, neighbourhood residential pattern and land use structure. In this study, an integrated framework for examining the fragmentation of dynamic and complex metropolitan areas, is proposed. The results indicate that the 49 highly fragmented sub-districts are distributed with large gated communities, industrial parks, green spaces and rivers/lakes. The fragmentation forms of the Wuhan metropolitan area include morphological, connectional and functional (variety and conflict) fragmentation, which constitute six scenarios. The geographical detector model manifests that urban fragmentation is the result of natural, socio–economic and construction factors. The increase in spatial debris driven by housing prices (q = 0.334), gross domestic product (q = 0.282), population density (q = 0.359), constructive index (q = 0.292) and road density (q = 0.314) has dramatically affected spatial organisation co–evolution. Additionally, there are synergistic enhancement effects between each pair of driving factors, i.e., bivariate or nonlinear interaction strengthens the impact of each other factor on the index of urban fragmentation. The strongest bivariate interaction is between housing prices and constructive index, with a value of 0.503. The largest nonlinear interaction is between constructive index and industrial index, with a value of 0.487. These interactions all further exacerbate urban fragmentation. These findings not only contribute to an integrated methodological framework, but also provide scientific implications for the purpose of sustainable urban development and cleaner production planning.
12. A win-win situation for environment and economy: Analysis of maximizing benefits in municipal sludge treatment plants
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138271
Abstract
The huge cost (economic cost and environmental cost) of treating municipal sludge has caused enormous pressure on China. How to balance economic cost and environmental benefits in China’s sludge treatment industry is an important issue that the government urgently needs to address. This article selects 9 types of municipal sludge treatment plants (MSTP) that can represent different treatment methods and scales in China, and attempts to help all provinces in China find the optimal solution for maximizing sludge treatment benefits (economic benefits and environmental benefits) under different constraints (economic constraints and environmental constraints). Firstly, this paper analyzes the economic and environmental costs and return of 9 types of MSTP. Secondly, we use the unguided Super-SBM model to combine the costs and return of 9 types of MSTP to measure the benefits of each plant. It has been found that under ideal conditions, medium Incineration treatment (IT) and large building material (BM) utilization are the most beneficial options for sludge treatment in China. Finally, we use a simple linear programming model to establish a constrained linear programming model for the environment and economy, substituting provinces that are divided into four categories under different constraint conditions into the model, and finding the optimal ratio for each type of province to build MSTP, in order to maximize benefits. Research has found that after adding constraints, the future development trend of municipal sludge treatment in China will mainly focus on small BM utilization and medium LA. This research result has universal applicability. As long as the constraints of this article are met, any country or province can adjust the construction proportion of municipal sludge treatment plants according to the research results of this article.
13. Matching ecosystem services supply and demand in China’s urban agglomerations for multiple-scale management
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 420, 25 September 2023, 138351
Abstract
The unprecedented urbanization rate has profoundly impacted ecosystem functions and increased the demand for ecosystem services. Moving towards sustainable cities requires an insightful understanding of ecosystem services supply and demand (ESSD). However, most ESSD studies ignore the spillover effects of ecosystem services, hindering sustainable urban agglomeration (UA) development from multiple spatial scale perspectives. This study evaluated the supply, demand, and sustainability of urban ecosystem services, including food production, water retention, soil retention, and carbon sequestration, by considering 19 UAs in China (including 236 cities). The results showed that the supply and demand of urban ecosystem services increased from 2000 to 2020, together with spatial heterogeneity. A decrease in the sustainability of food production was observed at medium UAs. Large UAs can achieve sustainability of all studied ecosystem services at both the UAs’ and national scales. However, the medium UAs in the northwest were unsustainable regarding water retention and carbon sequestration at the UAs’ scale. Land use/land cover (LULC) change was the key factor in ESSD change, followed by population. Finally, policy implications were proposed, including bringing ESSD into land use decision-making, reducing ecosystem service demand, implementing targeted restoration, and multiple-scale management.
14. The impact of industrial digital transformation on green development efficiency considering the threshold effect of regional collaborative innovation: Evidence from the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration in China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 420, 25 September 2023, 138345
Abstract
Promoting industrial digitalization and deepening regional collaborative innovation is essential for achieving urban green and sustainable development. This paper constructs a differential game model based on theoretical analysis and reveals the influence mechanism of industrial digitalization and regional collaborative innovation on urban green development efficiency (GDE). After that, this paper uses the entropy method, Super-SBM model, and improved gravity model to measure the level of industrial digitalization, urban GDE, and regional collaborative innovation, respectively. Then, this paper constructs the fixed-effects model, SDM model, moderating-effects model, and threshold model, then uses the panel data of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) urban agglomeration during 2011–2020 for empirical testing. The results show that: (1) industrial digitalization significantly improves urban GDE. (2) Overall, 2011–2015 is the rapid development period of BTH industry digitalization, and 2015–2020 is its stable development period. However, there are apparent spatial differences and imbalances. (3) Industrial digitalization has a significant spatial spillover effect that can enhance local and surrounding cities’ GDE. (4) Regional collaborative innovation can directly enhance urban GDE, and has a positive moderating effect on industrial digitalization to enhance urban GDE. (5) The regional collaborative innovation has two thresholds of 3.9851 and 6.6184. With the collaborative innovation level improving, the main effect intensity steadily increases.
15. Solid waste management techniques powered by in-silico approaches with a special focus on municipal solid waste management: Research trends and challenges
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 891, 15 September 2023, 164344
Abstract
Many technical, climatic, environmental, biological, financial, educational, and regulatory factors are typically involved in solid waste management (SWM). Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques have lately gained attraction in providing alternative computational methods for resolving problems of solid waste management. The purpose of this review is to direct solid waste management researchers taking an interest in the use of artificial intelligence in their area of study through main research elements such as AI models, their own benefits and drawbacks, effectiveness, and applications. The major AI technologies recognized are discussed in the subsections of the review, which contains a specific fusion of AI models. It also covers research that equated AI technologies to other non-AI methodologies. The section that follows contains a brief debate of the numerous SWM disciplines where AI was consciously applied. The article concludes with progress, challenges and perspectives in implementing AI-based solid waste management.
MÔI TRƯỜNG KHU CÔNG NGHIỆP
1. A multi-period design method for the steam and power systems coupling solar thermal energy and waste heat recovery in refineries
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137934
Abstract
It is imperative to reduce carbon emissions by comprehensively utilizing renewable energies and waste heat in refineries. However, the intermittent supply of solar thermal energy, the periodic changes of waste heat, and the variable demands of steam and electricity in refineries hinder optimal design and stable operation of the steam and power systems. In this work, an optimal design method for coordination of solar thermal energy and waste heat to produce steam and electricity in refineries was proposed, which features a multi-period mathematical programming model to synchronously determine the economy, the optimal capacity configuration, and the power scheduling scheme for the steam and power system. The influence of the serial and parallel structures of solar thermal energy supply, the model processing method for continuity of energy storage among different subperiods, and parametric analysis on the results were analyzed and discussed in detail. The results show that the cost of the solar thermal collectors and the energy storage system accounts for the significant proportion of the investment cost of the system. The cost of solar thermal collectors accounts for the largest proportion of the investment cost of the system, which is about 60% in the case study. The parallel structure of solar thermal energy supply can significantly reduce the total cost of the system. The coordination of solar thermal energy and waste heat recovery can jointly meet the steam demand to ensure the stability of the energy supply of the system. The comprehensive interactions and coordination between the solar steam generation systems, waste heat systems, energy storage systems, and demands are analyzed. The battery is necessary for short-time energy storage, whereas thermal energy storage should be used for either long-term or short-term energy storage. These results provide fundamental support for the optimal design of the steam and power systems in refineries by the comprehensive utilization of solar thermal energy and waste heat.
2. Multi-objective electricity cost and indirect CO2 emissions minimization in commercial and industrial buildings utilizing stand-alone battery energy storage systems
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 137987
Abstract
A large portion of global carbon emissions are attributable to electricity generation. Several previous studies indicate that both electricity cost and carbon emission reductions are not attainable with stand-alone battery energy storage systems for residential buildings. However, in this study, lithium-ion battery energy storage dispatch (charging and discharging) is optimized as a multi-objective decarbonization and cost-saving strategy in ten commercial and industrial facilities. The analysis tests 100 energy storage capacities, 5 discharge times, and 2 control strategies with and without enrollment in event-based demand response. Unlike smaller energy consumers, the results show significant indirect CO2 emissions reductions (>31%) paired with significant electricity cost reductions (>10%) are possible from stand-alone battery energy storage systems in a large commercial facility. Additionally, the results indicate that enrollment in the event-based demand response program and dispatch under the load shifting control strategy are always optimal to minimize both the discounted payback period and the indirect CO2 emissions.
3. Carbon emissions and decarbonisation: The role and relevance of fermentation industry in chemical sector
Chemical Engineering Journal, Available online 28 September 2023, 146308
Abstract
Fermentation industry is emerging as sustainable technological alternative to cater the production of various chemical building blocks which are commercially manufactured by petrochemical route. The primary reason for this major transition is global commitment towards decarbonisation of chemical sector, as their conventional fossil-based routes pose serious environmental threat. For instance, in 2022, the direct carbon dioxide (CO2) emission during synthesis of primary chemicals accounted for ∼ 920 Mt. CO2 is one of the prominent greenhouse gases (GHG’s), contributing majorly towards global warming effect and drastic climate change. Fermentation industry largely thrives on exploiting fermentable and organic carbon derived from edible and/or non-edible biomass and transforming them to valorised products using microbial cell factories. Therefore, the production of bio-based chemicals via this route is often associated with low or zero-carbon footprint, resulting in either carbon neutral or carbon negative products. This review focuses on different types of fermentative processes and their impact on carbon release and decarbonisation. It further discusses the relevance and contribution of fermentation industry as well as biological processes to provide a sustainable solution towards decarbonisation of chemical sector. Further, it showcases the advantages of some commercial proven and/or pipeline bio-based products over their conventional competitor fossil-based products, especially from an environmental viewpoint. Finally, advantages of biogenic CO2 from fermentation industry over other sources and CO2 removal from fermentation as a platform for carbon offsetting are covered.
4. Comparative environmental impact assessment of additive-subtractive manufacturing processes for Inconel 625: A life cycle analysis
Sustainable Materials and Technologies, Volume 37, September 2023, e00682
Abstract
This paper presents a life cycle assessment (LCA) approach to compare the environmental impacts of additive-subtractive manufacturing processes for Inconel 625. The LCA follows a cradle-to-gate methodology and employs the Eco-chain Mobius Software, in accordance with ISO 14044 standards. The chosen LCA model enables industries to develop sustainable production techniques by evaluating 18 environmental variables’ potential effects on human health, ecosystems, and resource availability. The LCA adopts the midpoint(H) approach from ReCiPe 2016 to comprehensively assess the environmental impacts. In the first case study, a plate is created using the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) method, followed by post-processing through drilling in both wet and dry environments. The dry condition results in a remarkable 24.23% reduction in environmental impact when the LCA is applied to the entire process, making it the most sustainable choice. In the second case study, a hollow cylinder is manufactured using the WAAM technique, and post-processing is conducted using turning processes under cryogenic, dry, and electrostatic minimum quantity lubrication (EMQL) conditions. The dry environment yields a 16.4% lower impact on the environment, establishing it as the most sustainable choice. Overall, the results from both case studies demonstrate that utilizing WAAM technology in a dry environment leads to the most sustainable manufacturing procedure for Inconel 625. This comparative analysis provides valuable insights to support the development of environmentally friendly production techniques in the manufacturing industry.
5. Linking internal environmental capabilities to sustainable competitive advantage in manufacturing SMEs: The mediating role of eco-innovation
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 137928
Abstract
With the world’s growing emphasis on environmental issues and the increased pressure on small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises (SMEs) to address such issues, sustaining competitiveness has become a critical concern for SMEs. Their organisational resources and capabilities must be configurated to align with environmental requirements to sustain their competitiveness. While mounting research has highlighted the importance of environmental capabilities in facilitating proactive environmental practices, it remains unclear how these capabilities can improve manufacturing SMEs’ sustainable competitive advantage (SCA). This study, therefore, has investigated how; green absorptive capacity, organisational capabilities and strategic environmental orientation have affected firms’ SCA, along with exploring the mediating effect of eco-innovation in such relationships. Using a sample of 176 manufacturing SMEs in Egypt, a cross-sectional survey approach was adopted to collect data on the research variables. The data were analysed using the Smart-PLS software application, and the results demonstrated the significant roles of; green absorptive capacity and strategic environmental orientation in facilitating eco-innovation, which in turn have helped SMEs sustain their competitive advantage. On the other hand, organisational capabilities did not appear to directly or indirectly affect firms’ SCA. Hence, this study may pique the interest of SME managers as it has emphasised the importance of strategic environmental orientation and green absorptive capacity in fostering eco-innovation and sustaining competitive advantage.
6. Effect of mandatory cleaner production audits on manufacturing firms’ environmental efficiency in China: Renovation or innovation?
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 137855
Abstract
Technological innovation is an important solution that can help improve environmental efficiency. However, the role of technological renovation in enhancing environmental efficiency has been ignored. This study provided initial evidence of the effects of cleaner production audits in China on manufacturing firms’ environmental efficiency, which was measured by the emissions of sulfur dioxide and chemical oxygen demand per total output. Cleaner production audits were used as exogenous shocks. Their impact was estimated using the staggered difference-in-difference method combined with samples of ever-treated or never-treated firms using propensity score matching. The findings showed that firms that conducted cleaner production audits (vs. those that did not) experienced 4.7% and 11.9% reductions in the emission intensities of sulfur dioxide and chemical oxygen demand, respectively. Cleaner production audit implementation significantly improved firms’ environmental efficiency. Additionally, a heterogeneous analysis showed that non-heavy polluters, small and medium-sized firms, and non-state-owned firms demonstrated the most improvement in environmental efficiency. Finally, the mechanism analysis results showed that firms’ technological renovation in the production process is the main solution for improving environmental efficiency. This is a feasible and cost-effective way of reducing resource consumption and pollutant emissions. Accordingly, a cleaner production audit plan for different countries should be formulated with a focus on technological renovation in the production process. It should entail clean-cut incentives to stimulate firms to perform technological innovation, thereby continuously improving firms’ environmental efficiency. This study sheds light on the environmental impact of cleaner production audits and regulated firms’ choices between technological renovation and innovation.
7. Mining-related environmental disasters: A High Reliability Organisation (HRO) perspective
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 137965
Abstract
Mining-related disasters can result in catastrophic, long-lasting impacts on the environment. They can also lead to loss of life, destruction of communities and financial loss. These events are continuing to occur, indicating that new methods of analysis and prevention are required. This paper describes the application of a novel approach, which is underpinned by the theoretical concepts derived from the study of High Reliability Organisations (HRO). These organisations are recognised for their ability to establish and maintain a “collective mindset”, a term that describes a situation where the actions of everyone in an organisation are structured by a collective desire to work towards shared goals. Research has also established common patterns that emerged from HROs, which are described as five hallmark characteristics (preoccupation with failure, reluctance to simplify, sensitivity to operations, commitment to resilience, deference to expertise).
In this paper, we analyse two mining-related environmental disaster case studies by reviewing the public inquiry reports that were published. We use the inquiry findings to evaluate the extent to which the companies involved had established a collective mindset with respect to avoiding environmental disasters. We also analyse how the actions they had undertaken to avoid an environmental disaster relate to the five hallmark HRO characteristics.
Although we recognise that technological factors are vital, the analysis shows focusing on organisational and human factors is also essential when developing strategies to mitigate the risks of environmental disasters. The results suggest that application of HRO theoretical concepts by mining companies can offer new strategies to increase organisational resilience and improve reliability in environmental performance when working towards elimination of mining-related environmental disasters.
8. Review on CO terminal treatment technologies in steel industry
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 418, 15 September 2023, 138231
Abstract
This paper reviews the methods for terminal treatment of CO components in the exhaust gas of the steel industry, including liquid absorption, solid catalytic and plasma oxidation method. High equipment cost for liquid absorption method and is limited by the energy consumption. Noble metal catalysts are expensive. Transition metals are cheap and widely used for the high efficiency, but the water resistance is poor. Plasma catalytic oxidation is rarely used alone due to uncontrollable products. Each technology is difficult to meet production requirements, so a combination of multiple technologies is adopted. Several processes were used to improve the hydrophobicity of transition metals. Hydrophobic coatings are difficult to balance reactivity and hydrophobicity, and reagents are expensive. Adding dissimilar metal atoms cannot adapt to high humidity environments for a long time. The plasma coupled catalytic process cannot completely eliminate the deactivation when encountering water. This paper focuses on the catalyst modification technology, analyzes the mechanism of water intoxication on the catalyst surface, summarizes the factors affecting the surface activity and finally predicts the change of surface bonding strength based on the HSAB theory, making prospects for the development of catalyst modification theory,and finally estimate the promotion of HSAB theory in production practice.
9. Establishing industrial community energy systems: Simulating the role of institutional designs and societal attributes
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138009
Abstract
The importance of decreasing industrial CO2 footprints has become evident, as also highlighted in COP26. As such, the transition to renewable energy in the industrial sector is essential to meet the targets. To this aim, establishing industrial community energy systems (InCES) where industries collectively invest in a shared energy system is an economically and environmentally attractive option. Yet, the emergence and continuity of such collective initiatives among industrial companies has neither received considerable attention in the scientific literature nor in practice. This research, as the first of its kind, aims to investigate institutional design options that allow for such collaboration to take place for the establishment and continuity of an InCES. Given the bottom-up and collaborative nature of such initiatives, we take an agent-based modeling and simulation approach, for the first time in this area, that incorporates the institutional and societal attributes that influence the formation and continuation of an InCES. We take data from an industrial cluster in Arak, one of the most prominent industrial cities in Iran. The results of this study confirm the economic feasibility of an InCES as compared to individual renewable energy investment in the cluster. The results also highlight the importance of flexible membership in increasing the number of investors (i.e., industrial companies) in such initiatives. Other important recommendations are: considering the installation of at least 15% extra capacity for the powerplant, restricting electricity consumption and enforcing on-time payment of monthly premium fees.
10. Decoupling effect and spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon emissions from construction industry in China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 419, 20 September 2023, 138243
Abstract
The construction industry is one of the most energy-intensive industries in China, which contributes to high carbon emissions and hinders efforts to reduce the emissions. The high energy consumption and emission have seriously constrained the growth of low carbon economy in China’s construction industry. And reducing the carbon emission from construction industry (CECI) has become the key to sustainable development and the achievement of “double carbon target”. The paper firstly decomposes the main influencing factors and calculates their effects by LMDI model. Then, the Tapio decoupling index is used to explore the decoupling relationship between carbon emissions and economic output. Finally, the spatial-temporal evolution of carbon emissions is analyzed through spatial autocorrelation theory. The results show that the carbon emissions from construction industry are highly increased by the construction employment rate (EM), and may be reduced by the energy intensity (EI) and carbon emission efficiency (CI). And the regions with better decoupling status are the eastern and central regions, which have relatively developed construction industry. Moreover, the spatial-temporal characteristic of carbon emissions is “high in the east and low in the west, high in the south and low in the north,” showing obviously regional differences.
11. Ultrafast photodegradation of textile industry dyes using efficient sulfide based ternary nanocomposites
Chemosphere, Volume 336, September 2023, 139100
Abstract
We developed novel zinc-cadmium-bismuth sulfide (Zn–Cd–Bi2S3) and Zn–Cd–SnS nanocomposites to fabricate a heterojunction by an easy chemical technique to improve photocatalytic degradation of textile dye. Crystalline size and lattice parameter are analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectrometer. The obtained strong diffraction peaks with various diffraction planes confirm the fabrication of a high crystal quality nanocomposite as well as the identification of its mixed crystal structure. The morphological information is studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Due to its higher surface energy, the as-prepared nanocomposite displayed agglomeration by adjoining to tiny particles. The roughness of surface is studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) used to study about presence of organic functional groups on the surface of nanocomposite. Using UV–Visible and photoluminescence spectra, the impact of shifting the positions of Sn and Bi ions on the optical characteristics is investigated. Thermal property of the nanocomposite is studied by thermogravimetric–differential thermal analysis (TG–DTA) at air atmosphere. We examine and compared the photocatalytic activity of Zn–Cd–Bi2S3 and Zn–Cd–SnS nanocomposites for the crystal violet (CV) dye. Under the sun light irradiation Zn–Cd–Bi2S3 nanocomposite demonstrated a highest percentage of degradation (88.5%) within a short period (120 min). The obtained photocatalytic results indicate that the active radicals •O2-, h+, and •OH- are favourable for the photocatalytic reaction. A possible photocatalytic mechanism for the dye degradation for the photocatalyst is proposed. Due to the narrow band gap, wide range of incident light captured by the heterostructure nanocomposite and the photogenerated electrons and holes is effectively separated in the Zn–Cd–Bi2S3.
12. Eco-industrial development strategies and characteristics according to the performance evaluation of eco-industrial park projects in Korea
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 416, 1 September 2023, 137971
Abstract
The economic performance of eco-industrial park (EIP) projects has been studied extensively in previous research; however, efforts to link EIP project performance with sustainable eco-industrial development (EID) strategies have been rarely considered. To bridge this gap, this study evaluated the performance of Korean EIP projects, promoted through three stages, based on the EID strategies using the ordinal scale evaluation method. Accordingly, the process of developing EIP projects in Korea was reviewed and the EID methodology was derived through previous research results. The analysis showed that 63.1% (32.8/58 points) of the EIP projects considered and/or applied the EID strategies to them, indicating that the Korean EIP Project Group suitably considered EID strategies, whereas other projects did not. The overall characteristics were: 1) The EIP projects with established initial EID strategies were more likely to produce better results (72.8%). 2) The projects with established initial strategies resulted in high economic performance. 3) The projects showed the high interest of EIP projects in strategies related to economic performance. 4) Strategies of high interest existed but did not lead to successful results. 5) Non-production process strategies were generally not implemented. 6) Performance depended on the ability of the project groups to enforce strategies. Our results showed the importance of applying EID strategies to EIP projects to achieve sustainable development, and suggest a revised systematic approach to develop EID strategies through analyzing the performance of EIP projects.
13. Industry 5.0 implications for inclusive sustainable manufacturing: An evidence-knowledge-based strategic roadmap
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 417, 10 September 2023, 138023
Abstract
Despite the hype surrounding Industry 5.0 and its importance for sustainability, the micro-mechanisms through which this agenda can lead to socio-environmental values are largely understudied. The present study strived to address this knowledge gap by developing a strategic roadmap that outlines how Industry 5.0 can boost sustainable manufacturing. The study first conducted a content-centric literature review and identified 12 functions through which Industry 5.0 can inclusively boost sustainable manufacturing. The study further developed a strategic roadmap that identified the complex contextual relationships among the functions and explained how they should be synergistically leveraged to maximize their contribution to sustainability. Results reveal that value network integration, sustainable technology governance, sustainable business model innovation, and sustainable skill development are the most driver and tangible implications of Industry 5.0 for sustainable manufacturing. Alternatively, renewable integration and manufacturing resilience are among the most dependent and hard-to-reach sustainable functions of Industry 5.0, and their materialization requires major strategic collaboration among stakeholders. The strategic roadmap outlines how Industry 5.0 stakeholders can leverage the technological and functional constituents of this agenda to promote sustainable manufacturing inclusively.
14. Environmental regulation, green innovation and high-quality development of enterprise: Evidence from China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 418, 15 September 2023, 138112
Abstract
Environmental regulation, as a safe line of defense for the ecological environment, is an important practical exploration to guide green innovation and to promote high-quality development of enterprise. This research examines the impact of environmental regulation on high-quality development of enterprise and the realization path based on the data of Chinese A-share listed enterprises from 2010 to 2020. The fixed-effect model reveals a significant positive correlation between environmental regulation and high-quality development of enterprise. Moreover, the chain intermediation model is used to examine the realization path. Specifically, environmental regulation hinders enterprises’ green management innovation and thus has a negative impact on high-quality development of enterprise, which is manifested as a masking effect. Environmental regulation has a positive impact on the high-quality development of enterprise through enhancing green technology innovation or the intermediation chain of “promoting green technology innovation – driving green management innovation”. Heterogeneity analysis reveals that environmental regulation has a facilitating effect on the high-quality development of enterprises for non-state-owned enterprises, and enterprises within the carbon emission trading pilot areas. In addition, environmental regulation has the strongest promoting effect on high-quality development of enterprise in the mature stage, followed by the growth stage. The research provides actionable paths for the government to optimize the institutional system of ecological environment construction and accelerate the modernization process of environmental governance.
15. Environmental taxes under mixed duopoly: The roles of privatization and foreign eco-technology
Economic Modelling, Volume 126, September 2023, 106373
Abstract
Governments usually impose environmental taxes to control pollution. This research theoretically investigates the welfare effect of privatization when a public firm and a private firm buy an abatement technology from a foreign eco-technology innovator in response to an environmental tax levied by the domestic government. Our results show if the environmental tax rate is sufficiently low (high), then privatization can lead to a lower (higher) eco-technology price, and thus privatization is desirable (undesirable) for social welfare. Moreover, while privatization clearly increases profits for both firms, it reduces consumer surplus and environmental tax revenue. Before privatization, higher environmental tax rates do not necessarily reduce total emissions. After privatization, higher environmental tax rates always reduce total emissions. We also find that privatization decreases total industry emissions when the harmfulness of emissions is low. However, when the harmfulness of emissions is high, the relationship between changes in total industry emissions after privatization and the environmental tax rate is not monotonic.
16. Reducing the environmental impacts of Brazilian chicken meat production using different waste recovery strategies
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 341, 1 September 2023, 118021
Abstract
Chicken meat has achieved significant index rates worldwide, with Brazil leading production and exports. The agribusiness significance has led to strengthening attention to the environmental burdens produced by the poultry industry. This research considered reducing the environmental impacts in the life cycle of Brazilian chicken meat regarding strategies for recycling waste from the production process. An attributional cradle-to-gate life cycle assessment was performed, with the functional unit of 1 kg of slaughtered and unpacked chicken meat. The two suggested scenarios used: i) chicken bedding for biogas production and ii) chicken carcass waste as meat meals in feed production. Handling poultry litter for biogas production avoided methane and ammonia emissions, reducing over 50% of the environmental indicators of Climate Change, Terrestrial Acidification, and Freshwater Eutrophication. Reuse poultry waste to produce meat meals reduced from 12% to 55% in all impact categories, decreasing emissions from carcasses destined for decomposition in landfills and using less raw materials from bovine sources. Investigating the environmental performance of the chicken meat production chain encouraged the circularity of natural resources and waste recovery strategies in the system boundary, thus helping to accomplish Sustainable Development Goals 7, 9, 12, and 13 of the UN Agenda 2030.
CHUYÊN TRANG QUẢN LÝ MÔI TRƯỜNG
Tạp chí Môi trường và Đô thị Việt Nam