Ban biên tập Chuyên trang Quản lý Môi trường, Tạp chí Môi trường và Đô thị Việt Nam trân trọng giới thiệu tới quý độc giả Công bố quốc tế lĩnh vực môi trường số 35-2024.
Về quản lý môi trường
– Nguồn gốc của sự khác biệt về phát thải carbon giữa Trung Quốc và Hoa Kỳ: Một nghiên cứu định lượng dựa trên chuỗi giá trị toàn cầu.
– Tiết lộ sức mạnh của sự đoàn kết: Một cuộc kiểm tra mới về hợp tác khu vực trong việc giảm thiểu ô nhiễm không khí.
– Phước lành hay tai họa? Vai trò của đổi mới công nghệ kỹ thuật số trong hiệu quả phát thải carbon.
– Một chương trình linh hoạt đa mục tiêu mạnh mẽ mới lạ để thiết kế một mạng lưới chuỗi cung ứng quần áo bền vững khép kín.
– Tác động của cài đặt mô hình chất lượng không khí đối với việc đánh giá các chiến lược giảm phát thải để hạn chế ô nhiễm không khí.
– Đánh giá tác động môi trường của đầu tư năng lượng sạch ở Pakistan bằng mô hình tự hồi quy phân phối động.
– Phân tích toàn cầu về các sáng kiến kinh tế tuần hoàn: tính bền vững yếu hay mạnh?
– Tính nghiêm ngặt của chính sách môi trường, CNTT-TT và đổi mới công nghệ để đạt được sự phát triển bền vững: Đánh giá tầm quan trọng của quản trị và cơ sở hạ tầng.
– Mở khóa tác động theo thời gian của tính dễ bị tổn thương năng lượng, phát triển tài chính và toàn cầu hóa chính trị đối với tính bền vững môi trường ở Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ: Bằng chứng từ các chỉ số ô nhiễm khác nhau.
Về môi trường đô thị
– Làm thế nào để đi từ đỉnh đến trung hòa? Quan điểm từ phân tích bù đắp phát thải tiêu thụ năng lượng ở Bắc Kinh-Thiên Tân-Hà Bắc Agglomeration.
– Lựa chọn loài rừng đô thị để cải thiện lợi ích sinh thái ở các thành phố Ba Lan – Tiềm năng thực tế và dự báo.
– Đặc điểm và tác động của đô thị hóa đất dốc toàn cầu từ năm 2000 đến năm 2020.
– Tăng cường khả năng phục hồi trong quản lý nước mưa đô thị thông qua kiểm soát dự đoán mô hình và sơ đồ bố trí tối ưu dưới các sự kiện mưa cực đoan.
– Không đồng nhất không gian của ảnh hưởng của các mô hình mạng lưới sông đối với chất lượng nước ở thành phố có mức độ đô thị hóa cao.
– Tác động của biến đổi khí hậu đối với cường độ và tần suất lũ lụt đô thị dưới các kịch bản và mô hình không chắc chắn.
– Tác động hiệp lực của nhiệt độ cao và độ ẩm tương đối đối với các trường hợp tử vong không do tai nạn ở các mức độ đô thị hóa khác nhau.
– Mối liên quan giữa phơi nhiễm PM2.5 trong khí quyển và nguy cơ sức khỏe gây ung thư: Dữ liệu giám sát từ năm có mức thấp nhất được ghi nhận ở Bắc Kinh, Trung Quốc.
– Đánh giá nguy cơ tổn thương sức khỏe môi trường vi mô tàu điện ngầm từ góc độ kết hợp: Trường hợp của Nam Kinh, Trung Quốc.
Về môi trường khu công nghiệp
– Tái xem xét mối liên hệ giữa tài chính hóa và hiệu quả tài nguyên thiên nhiên dưới góc độ phát triển tài chính và tối ưu hóa công nghiệp xanh.
– Loại bỏ carbon dioxide có thể dẫn đến việc sử dụng quặng sắt cấp thấp hơn trong ngành thép khử cacbon phát thải ròng âm.
– Phân tích không gian địa lý về ô nhiễm kim loại độc hại trong nước ngầm và các rủi ro sức khỏe liên quan ở khu vực công nghiệp phía dưới dãy Himalaya.
– Xử lý nước thải ngành dược phẩm để tái sử dụng nước ở Jordan bằng cách sử dụng vùng đất ngập nước nhân tạo lai.
– Một cuộc điều tra về tiền đề và hậu quả của việc nội bộ hóa giá trị xanh giữa các doanh nghiệp được lấy mẫu ở Vương quốc Anh.
– Các tác động hiệp lực khác nhau của việc giảm phát thải tiền chất đối với PM2.5 và O3 ở một thành phố công nghiệp điển hình với sự phân bố phức tạp của khí thải.
– Chuyển đổi kỹ thuật số và đổi mới carbon thấp của doanh nghiệp: Một góc nhìn mới từ động lực đổi mới.
– Sinh học Chlorella vulgaris – môi trường khắc phục nước thải thực phẩm và đồ uống từ các ngành công nghiệp ở Mexico: Kết quả và quan điểm hướng tới tính bền vững và nền kinh tế tuần hoàn.
– Quản lý định hướng bền vững trong các doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ. Một phân tích đa cấp ở Liên minh Châu Âu.
– Giám sát lượng khí thải carbon của doanh nghiệp công nghiệp carbon cao trên thị trường carbon: Một cách tiếp cận đa tín nhiệm sử dụng dữ liệu lớn có sẵn bên ngoài.
CHUYÊN TRANG QUẢN LÝ MÔI TRƯỜNG
Tạp chí Môi trường và Đô thị Việt Nam
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT / QUẢN LÝ MÔI TRƯỜNG
1. Impact of pollution prevention practices and green environmental practices on sustainable performance: Empirical evidence from Chinese SMEs
Environmental Research, Volume 255, 15 August 2024, 118991
Abstract
Adequate protection of the environment is one of the hot spots of concern for all sectors of society due to severe environmental pollution. The solution to this issue is friendly management of the environment. With the rapid growth of Chinese Manufacturing SMEs for economic development, environmental pollution and abuse of resources are arising. To resolve these issues, Chinese manufacturing SMEs are accelerating the implementation of green innovation in their industries. However, it is a complex task that involves enterprise, government, and social considerations.
Therefore, it is essential to identify the green drivers for this implementation. With a focus on China’s current situation from previous research and views from experts, this study aims to investigate how Chinese Manufacturing Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) are responding to resource misuse and environmental pollution by implementing green innovation, emphasising the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in improving environmental performance. This study primarily looks into the factors that influence the adoption of green innovations by analysing the growth paths of Chinese SMEs operating in highly polluting industries over a longer time frame than five years. Artificial Intelligence is a valuable tool for solving the issues of ecological degradation. A quantitative method has been implemented for the Chinese companies’ samples from the deeply polluting industries for more than five years. The findings of this paper advise that the average board size, the governing board meetings, and organizational performance are positively connected with the Chinese firms’ environmental process. Board independence and diversity of gender have irrelevant associations with ecological performance.
A convenient threshold regression model has been used to accumulate the respondents’ data. It also reveals that larger board sizes and more frequent governing board meetings are positively associated with improved environmental performance among these firms. The findings state the critical implications for the firm executives, policymakers, environmental activists, and regulators. This result supports the insight drained from the resource dependence, stakeholder, firm agency, and legitimacy theories.
2. The roots of carbon emission differences between China and USA: A quantitative study based on global value chains
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121476
Abstract
China and the USA, as preeminent contributors to global carbon emissions, demonstrate discernible differentials in both magnitude and trajectories of their respective carbon outputs. This article employed two methods, Structural Decomposition Analysis (SDA) and Quantitative Structural Modeling, to scrutinize the underpinnings of these disparities through the lens of the global value chain. Drawing upon data from the World Input-Output Database (WIOD), our analysis revealed that the compounded influences of output composition, input intensity, input composition and input origin collectively elevated China’s aggregate carbon footprint from 2000 to 2014, while the scale effect made China’s carbon emissions lower than of the USA.
Notably, China’s carbon emissions surpassed those of USA, with the gap accentuating over time. The quantitative results of the structural model showed that the difference in carbon emissions between China and USA predominantly stem from disparities in productivity, production technology, factor intensity, factor endowment and direct carbon intensity. Differences in trade costs exhibited some discernible impact, their influence remains relatively marginal, whereas distinctions in consumption behaviors and trade imbalances minimally contribute to the observed differentials. These findings have important policy implications for global carbon reduction efforts and China’s trajectory towards a low-carbon economic paradigm.
3. Does natural resource dependence restrict green development? An investigation from the “Belt and road” countries
Environmental Research, Volume 255, 15 August 2024, 119108
Abstract
Addressing natural resource dependence is integral to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals by promoting economic diversification, environmental sustainability, and climate resilience. This study explores the effect of natural resource dependence on green development by adopting the balanced panel dataset from the “Belt and Road” countries from 2005 to 2019. Notably, the novelty of our analysis lies in the empirical analysis using instrument-based techniques that consolidate the “green development curse hypothesis” in the Belt and Road countries. The mechanism analysis reveals that natural resource dependence curbs green development by weakening innovative capability, disturbing institutional quality, reducing population density, and crowding out human capital.
Further, the dynamic panel threshold model handling endogeneity verifies the nonlinear relationship between natural resource dependence and green development. Interestingly, digital trade offers greater “resilience” than traditional trade, correcting the resource curse dilemma. Finally, heterogeneity analyses indicate that the green development curse hypothesis only exists in countries with high-level environmental regulations and resource-based countries.
4. Unveiling the power of unity: A novel examination of regional cooperation in mitigating air pollution
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121556
Abstract
Amidst escalating environmental concerns, regional cooperation has emerged as a potent strategy for environmental preservation. Yet, the potency of such cooperation in curbing air pollution remains largely unexplored and nebulous. Drawing upon a decade-long (2010–2019) new data from the dynamic Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA), this study seeks to fill these knowledge gaps. Our findings underscore the transformative potential of regional cooperation in mitigating air pollution. By catalyzing technological advancements, fostering structural shifts in businesses, and reshaping land-use patterns, regional cooperation paves the way for a cleaner, healthier environment.
A deeper dive into the heterogeneity reveals that “top to bottom” city agreements within regional cooperation frameworks significantly enhance air quality. While institutional and economic collaborations prove instrumental in reducing air pollution, social cooperation appears to have a lesser impact. Research findings indicate that the future will necessitate strengthening formal, institutionalized regional cooperation to address potential challenges posed by environmental pollution.
5. Information consumption city and carbon emission efficiency: Evidence from China’s quasi-natural experiment
Environmental Research, Volume 255, 15 August 2024, 119182
Abstract
The transformation of public consumption patterns has become a burning question, but there are few studies on public consumption patterns. Therefore, evaluating the impact of Information consumption city (ICC) policy on carbon emission efficiency holds significant implications. This study settles on 104 pilot cities in China from 2006 to 2020 to assess the impact and the response mechanism of ICC policy on carbon emission efficiency through the time-vary Difference-in-Difference (DID) model.
The result shows that: (1) ICC policy significantly promotes the local carbon emission efficiency, which remains robust after a battery of sensitivity tests. (2) It improves carbon emission efficiency through production factors agglomeration effect, industrial structural changing effect, innovation promotion effect, and environmental attention effect; (3) The direct impact of ICC policy on carbon emission efficiency varies across regions with different information consumption and carbon emission base. (4) ICC can improve carbon emission efficiency through the joint implementation of smart city (SC), new urbanization (NU), ecological civilization city construction (EC), Belt and Road Initiative (BR), Broadband China (BC), low-carbon city pilot policy (LCC), and air quality standards (AQS) policy.
6. Blessing or curse? The role of digital technology innovation in carbon emission efficiency
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121579
Abstract
Digital technology advancement provides a significant impetus to achieve China’s “dual-carbon” goals, yet it also gives rise to a series of challenges. Therefore, studying the relationship between digital technology innovation and carbon emission efficiency is of paramount importance. This study theoretically analyzes and empirically tests the influence of digital technology innovation (DTI) on total factor carbon emission efficiency (TFCE) using panel data from 268 Chinese cities between 2006 and 2021. The results indicate that: (1) DTI exhibits a “U-shaped” pattern on urban TFCE, with a decrease followed by an increase. (2) Conventional technological innovation (TI) also displays a “U-shaped” relationship with TFCE, with the turning point occurring earlier than that of DTI. DTI surpasses TI in bringing about later-stage improvements in carbon emission efficiency. (3) Mechanism tests reveal that digital technology innovation indirectly affects TFCE through energy effects, technological effects, structural effects, and regulatory effects. (4) The impact of DTI on urban TFCE varies significantly due to differences in geographical location and resource endowments. (5) The development of urban polycentricity advances the turning point at which DTI enhances TFCE while amplifying both the initial “pro-carbon” effect and the subsequent “carbon reduction” effect of DTI. (6) DTI has a spatial spillover effect on urban TFCE. This study provides empirical evidence and policy recommendations for policymakers to advance the digitalization, greening, and decarbonization transformation of cities.
7. Assessing the impact of environmental regulations on environmental performance in Chinese cities: A spatial Stochastic Frontier Model with endogeneity analysis
Environmental Research, Volume 255, 15 August 2024, 119123
Abstract
The Chinese government has implemented environmental regulations to address the deterioration of air quality associated with rapid industrialization. However, there is no consensus on whether environmental regulations are beneficial to environmental performance. The technical challenges related to endogeneity and spatial correlation may bias the estimation of the emission reduction effect of regulations. In this study, we comprehensively evaluate the environmental performance of sulfur dioxide regulations in Chinese cities using a novel stochastic frontier model that introduces the single control function to correct estimation errors caused by spatial spillovers and endogeneity.
Our analysis emphasizes that insufficient resolution of endogeneity or spatial spillovers may lead to underestimation or neglect of the environmental performance improvements achieved by these regulations. On the contrary, our revised research results indicate that regulations aimed at reducing sulfur dioxide emissions not only successfully control sulfur dioxide emissions, but also have a positive impact on reducing carbon emissions. In addition, we conduct in-depth research on the mechanisms by which environmental regulations improve performance by stimulating green technology innovation and promoting industrial structure upgrading. Based on our research findings, we propose policy recommendations to establish a city cooperation mechanism of technology exchange to achieve synergistic emission reduction and strengthen regional factor circulation.
8. A novel multi-objective robust possibilistic flexible programming to design a sustainable apparel closed-loop supply chain network
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121496
Abstract
Designing a sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain (CLSC) network is imperative for the apparel industry, given its escalating adverse effects on economic, environmental, and social dimensions. In this study, a novel tri-objective location-allocation optimization model is specifically developed for designing a sustainable apparel CLSC, incorporating the industry’s unique facilities. The aim of the model is to simultaneously minimize the costs and negative environmental impacts while maximizing social benefits under demands and returns uncertainty. A notable research contribution lies in addressing the unique challenges of treating different types of returns, including commercial, End Of Use (EOU) and End Of Life (EOL) returns due to their uncertain quality and quantity. Additionally, the model optimizes the environmental performance levels of production facilities, a novel aspect in the apparel CLSC research. Moreover, the flexibility of constraints related to the demand fulfilment is considered.
To cope with such flexibility and uncertainties, a new hybrid robust possibilistic flexible programming model is developed, by extending the previous methodologies. A core innovation of this solution approach lies in the pioneering utilization of hexagonal fuzzy numbers for uncertain epistemic parameters, making a significant advancement in the field of CLSC. Comparative analysis with the similar studies demonstrates the superiority of the proposed model, incorporating hexagonal fuzzy numbers over the method using triangular fuzzy numbers. Furthermore, AUGMECON method using lexicographic optimization is applied to handle the multi-objective model. The application of the proposed model is shown focusing on Southwestern Ontario in Canada. The results reveal that commercial and EOU returns have a more detrimental impact on economic, environmental, and social sustainability aspects compared to EOL returns.
9. Impact of air quality model settings for the evaluation of emission reduction strategies to curb air pollution
Environmental Research, Volume 255, 15 August 2024, 119112
Abstract
For air quality management, while numerical tools are mainly evaluated to assess their performances on absolute concentrations, this study assesses the impact of their settings on the robustness of model responses to emission reduction strategies for the main criteria pollutants. The effect of the spatial resolution and chemistry schemes is investigated. We show that whereas the spatial resolution is not a crucial setting (except for NO), the chemistry scheme has more impact, particularly when assessing hourly values of the absolute potential of concentrations. The analysis of model responses under the various configurations triggered an analysis of the impact of using online models, like WRF-chem or WRF-CHIMERE, which accounts for the impact of aerosol concentrations on meteorology. This study informs the air quality modeling community on what extent some model settings can affect the expected model responses to emission changes. We suggest to not activate online effects when analyzing the effect of an emission reduction strategy to avoid any confusion in the interpretation of results even if an online simulation should represent better the reality.
10. Assessing the environmental impacts of clean energy investment in Pakistan using a dynamic autoregressive distributed lag model
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121549
Abstract
In this study, the authors projected the impacts of clean energy investment on environmental degradation by applying a novel and dynamic Autoregressive Distributed Lag (DARDL) model for Pakistan from 1990 to 2022. Most researchers have used ecological footprint or CO2 emissions indicators to look at how clean energy investment affects environmental degradation, which primarily represents contamination induced by humans’ consumption patterns and does not consider the impact of the supply side. Against this background, the study scrutinized the dynamic interaction between clean energy investment and environmental sustainability using the load capacity factor (LCF) as an ecological indicator in Pakistan, including economic growth, population density, trade openness, urbanization, and industrialization in the analysis.
The long-run estimates from DARDL indicate that a 1 percent upsurge in clean energy investment mitigates environmental degradation by approximately 0.42 percent on average, controlling for other factors. Further, the study also revealed that a 1 percent increase in clean energy investment diminishes dirty energy consumption by approximately 0.45 percent. The validity of the findings is confirmed using alternate methods, i.e., KRLS. The study recommends that Pakistan prioritize investment in clean energy projects to promote environmental sustainability and enforce environmental regulations to reduce the adverse externalities associated with dirty energy activities.
11. A global analysis of circular economy initiatives: weak or strong sustainability?
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 467, 15 August 2024, 142830
Abstract
In the face of climate change, the circular economy is attracting the attention of public authorities, international institutions, industry and academia. There is currently no consensus on its definition and it varies according to the sectors and actors. The objectives of this work are threefold: (i) to identify all the discourses and initiatives attributed to the circular economy in order to situate them according to whether they belong to weak or strong sustainability; (ii) to enhance the value of this information by centralizing it, and creating tools to facilitate its exploration and access; (iii) to analyze how these initiatives allow circular economy to address global sustainability. Questions regarding data sources and processing of this information were raised to facilitate the collection of relevant data.
This work focuses on information published on social networks, in particular Twitter called X now. Several data processing techniques such as text mining, geocoding and knowledge graph generation are applied. Data visualization tools are used to show the distribution of the data on a spatial, thematic and temporal level. The results obtained confirm the over-representation of circular economy practices based on weak sustainability in developed countries, while circular economy initiatives based on strong sustainability are most common in the Global South. This paper provides evidence on the social contribution of circular economy, which is less addressed in the technocentric approach.
12. Environmental policy stringency, ICT, and technological innovation for achieving sustainable development: Assessing the importance of governance and infrastructure
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121581
Abstract
Achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) has garnered significant attention from academia and policymakers worldwide. In this study, we examine the impact of ICT, technological innovation (TI), and environmental policy stringency (EPS) on SDI, considering the moderating role of governance quality (GQI) and transport infrastructure (TIS). A comprehensive dataset of 17 advanced nations is utilized from 1996 to 2021. To capture the dynamic and extreme marginal impacts of these policy instruments on SDG attainment, we employ the advanced technique of Feasible Generalized Least Square (FGLS). The results demonstrate that ICT has a positive and significant effect on SDGs, particularly when combined with high levels of governance quality (GOV) and transport infrastructure (TIS). Likewise, TI has a positive impact on SDGs, especially in the presence of strong governance.
Furthermore, EPS exhibits a positive association with SDGs. The findings also reveal that while governance hurts SDGs, this effect diminishes when combined with higher levels of ICT, TI, and EPS, and when TIS positively moderates the relationships. The robustness estimations using DOLS and PCSE methods validate the FGLS findings. These results underscore the importance of ICT, TI, and EPS in advancing sustainable development. Moreover, they highlight the significance of good governance and robust transport infrastructure in maximizing the positive effects of these factors. These findings hold implications for policymakers and stakeholders involved in promoting sustainable development.
13. Specialized, diversified agglomeration and CO2 emissions —An empirical study based on panel data of Chinese cities
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 467, 15 August 2024, 142892
Abstract
Taking proactive steps to control carbon emissions (CO2) in the industrial sector is crucial for meeting the “30.60” carbon reduction commitment expediently. This study meticulously investigates the correlation and underlying mechanisms between industrial agglomeration and CO2 emissions, employing the fixed-effect model and regulatory-effect model across 283 cities from 2006 to 2019.The findings reveal the following: Firstly, specialized agglomeration exacerbates CO2 emissions, while diversified agglomeration substantially contributes to their reduction. Notably, the carbon reduction effect of industrial diversification is particularly pronounced in the southern region, carbon peak region, and industrial transfer region.
Secondly, delving into mechanisms uncovers that specialized agglomeration’s exacerbating effect stems from labor misallocation, whereas diversified agglomeration mitigates CO2 emissions by enhancing both labor and capital allocation. Thirdly, regarding spatial spillover effects, specialized agglomeration not only increases CO2 emissions locally but also elevates nearby emissions, whereas diverse agglomeration not only reduces local CO2 emissions but also radiates carbon reduction in adjacent areas. To fully realize the benefits of agglomeration in reducing carbon emissions and promoting regional development, the government should thus support diversified agglomeration, remove any barriers preventing the flow of production factors, and fortify interregional industrial division and cooperation.
14. Unlocking time-quantile impact of energy vulnerability, financial development, and political globalization on environmental sustainability in Turkey: Evidence from different pollution indicators
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121499
Abstract
Increasing energy vulnerability can cause environmental pollution by increasing fossil fuel consumption. If it leads to cost-cutting-oriented industry growth, financial development can lead to environmental regulations being ignored, compromising environmental quality. Political globalization and economic growth can increase short-term environmental pressures, straining long-term ecological balance and causing habitat loss and pollution. This study investigates the impact of energy vulnerability, financial development, and political globalization on environmental sustainability in Turkey for the 2000–2019 period using with wavelet quantile-based techniques. According to results, while the negative effect of energy vulnerability on environmental quality is lower in the short term, the size of the effect increases in the medium and long term.
In addition, at low quantiles of environmental quality, the negative effect of financial development is low in the short and long term, while the effect becomes evident in the long term. Moreover, the effects of political globalization on environmental quality are positive in all quantiles. Additionally, the harmful effects of economic growth are more evident at lower quantiles of environmental quality. Turkey should increase its clean energy investments by using its geographically advantageous location. Policymakers should also prioritize environmental regulations and promote sustainable practices in industries. Incentives for cleaner production technologies and environmentally friendly initiatives can help steer the financial sector towards more responsible and environmentally friendly practices. Additionally, the study suggests that increasing institutional capacity and aligning national policies with international agreements can accelerate the positive effects of political globalization.
15. Energy transition dynamics amid policy uncertainty, environmental regulations, and Geopolitics: Evidence from China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 467, 15 August 2024, 142992
Abstract
The time-varying dynamics of the transition to renewable energy reflect the effectiveness and efficiency of energy policy. This paper investigates renewable energy transition behavior in China using Markov regime-switching models. Two distinct phases, expansion and contraction, are identified based on the growth rates of renewable energy consumption share. We find that since China started its new-energy national strategy in 2005, there has been an extended period in which it has been in the expansion state, although it occasionally reverts to a contraction state. Intriguingly, we uncover that the timing of transition state changes can be explained by the changes in policy-related, market-based instruments and risk-related indexes. These findings present implications for policymakers in developing more precise and effective policies, that drives investment choices to align with the goal of a sustainable energy system.
16. Environmental judicial reform and corporate investment behavior – Based on a quasi-natural experiment of environmental courts
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121640
Abstract
Ensuring the effectiveness of environmental legislation and regulations necessitates enhancing the professional caliber of the environmental judiciary. Utilizing a multi-period difference-in-differences model, we explore the impact of environmental judicial reforms, exemplified by the establishment of environmental courts, on corporate investment behavior. We find that firms in regions with established environmental courts significantly increase their environmental investments and productive investments, while financial investments remain unaffected. Mechanism testing reveals that the environmental court affects corporate investment by strengthening local government environmental enforcement and promoting public environmental participation.
Furthermore, the marginal effect of environmental courts is more pronounced in regions with fewer environmental regulations and lower economic development levels, as well as in state-owned enterprises. Compared to collegiate benches, environmental resources judicial tribunals exert a greater influence on corporate investment behavior. This study adds to the micro-economic analysis of environmental judiciary by providing empirical evidence on how formal institutional frameworks impact corporate investment behavior.
17. A critical review of climate change mitigation policies in the EU – based on vertical, horizontal and policy instrument perspectives
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 467, 15 August 2024, 142972
Abstract
The European Union (EU) has consistently held a prominent global position in climate governance. This paper compiles 152 climate neutrality policies issued by the European Commission (EU Commission) and employs a systematic analytical framework including “Vertical Policy Hierarchy – Horizontal Policy Path – Systematic Policy instruments” to conduct an in-depth analysis of the EU’s climate neutrality policy system.
This study produces several findings as follows: First, the EU’s climate neutrality policy hierarchy is characterized by a structure comprising “Long-Term Planning – Specific Measures – Financial Support”. Second, the EU’s policy formulation process for climate neutrality emphasizes the integration of a multi-party engagement mechanism involving “Nongovernmental Level – Regional Level – National Level – Transnational Level – Supranational Level”, while extensively employing a “framework-content” policy-making methodology. Third, the EU’s climate neutrality governance is guided by the dual objectives of achieving a “Cleaner Energy Structure” and “Recover Ecological Environment” pursuing a broad-ranging and multi-tiered policy pathway towards climate neutrality. Fourth, the EU leverages a combined approach of mandatory measures and guiding policies to propel the climate neutrality governance process, aspiring to achieve breakthroughs in new energy technology innovation through climate neutrality governance, thereby solidifying its international standing. Moreover, this study provides an outlook on the future of the EU’s climate neutrality policy governance, positing that the EU’s emphasis on climate neutrality governance will remain undiminished, with a heightened focus on guiding policies and an emphasis on the roles of enterprises and the public in advancing the realization of climate neutrality.
URBAN ENVIRONMENT/ MÔI TRƯỜNG ĐÔ THỊ
1. How far need to go from peak to neutrality? Perspective from energy consumption emission offset analysis in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Agglomeration
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 468, 25 August 2024, 143119
Abstract
Carbon emissions elimination in the rapid urbanization areas contributes to regional sustainable development and global climate change mitigation. With the target of carbon neutrality, the global top-class Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration which confronts with the dual pressure of excess carbon emissions and shrink ecological space has increased its carbon reduction coordination cooperation, among which energy consumption carbon emission control and natural resource sink maintenance have been recognized as the key strategy. However, the study on carbon balance prediction is lack and the amount of energy consumption carbon emissions in the future can be offset by the ecological carbon sink is still unknown.
To estimate the gap to carbon neutrality, this study proposes a framework for carbon offset analysis and prediction which takes various carbon emission scenarios and the potential of natural resource on carbon reduction into consideration. After the framework conduction in the agglomeration, it is revealed that the regional least carbon emissions of 29.51 Mt mainly derive from the population and economic growth brought by urbanization process, while the carbon sink predicted to be 2552.31 Kt is still far to cover the emissions. With the regional carbon offset rate decline from 0.68% to 0.63%, the ecological carbon sink in Beijing will offset 1.21% of its carbon emission, while the least ecological space keep city Tianjin is predicted to suffer the lowest offset rate of 0.09%. The research results contribute to recognize the key factors on carbon emission control and key areas for carbon maintenance in following years, as well as narrowing the gap to neutrality with both consideration of carbon emission reduction and sink maintenance.
2. Systematic coupling and multistage interactive response of the urban land use efficiency and ecological environment quality
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 365, August 2024, 121584
Abstract
Rapid urbanization and industrialization have greatly contributed to boosting regional economic growth and mitigating the problem of poverty, but blind expansion of cities and towns has not only caused the inefficient use of urban land resources but also caused the deterioration in the urban ecological environment. Within the current context of emphasizing high-quality development, achieving synergy between the efficient use of urban land and ecological environmental protection is an urgent task for promoting new urbanization construction. In this study, cities in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River (URYR) were adopted as the research object, a theoretical analysis framework for the urban land use efficiency (ULUE) and ecological environment quality (EEQ) was established, the ULUE was measured by using the Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) model, the coupling coordination and interactive corresponding response relationship between the ULUE and EEQ were analyzed, and the influencing factors of the coupling coordination between these two systems were explored by using the random forest model.
The following conclusions can be obtained: in 2020, compared with those in 2006, both the ULUE and EEQ were improved, and the two systems exhibited interactions and significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity. The coupling coordination degree (CCD) between the ULUE and EEQ could facilitate maintaining the original state, and the transfer of the CCD exhibited a significant spatial correlation with the state of neighbouring cities. The effect of the ULUE on the EEQ indicated nonlinear characteristics, while the effect of the EEQ on the ULUE was manifested as inhibition initially and then promotion. The random forest regression results showed that the population density, landscape agglomeration and connectivity, market conditions, government intervention, and industrial institutions are the key influencing factors of the CCD. Finally, this study provides policy implications for innovative urban land use modelling, environmental regulation, and industrial transformation and upgrading.
3. Resource-based transformation and urban resilience promotion: Evidence from firms’ carbon emissions reductions in China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 468, 25 August 2024, 143118
Abstract
The current research investigating the effectiveness of policy-driven transformation in resource-based cities has focused mainly on city-level impacts and has overlooked firm-level evidence. This paper filled this gap by focusing on its impact on firm-level carbon emissions. Drawing on the quasi-natural experiment of China’s reform of resource-based city transformation, we utilize a difference-in-differences (DID) model based on nationwide firm-level tax survey data from 2009 to 2016. The findings indicate a noteworthy reduction in firms’ carbon emissions due to the reform, particularly in growing-type resource-based cities and within the manufacturing industry. The empirical results provide evidence that the implementation of the “Plan” has effectively enhanced the level of urban resilience. Moreover, the findings demonstrate stronger effects on large firms, publicly owned firms, and firms in municipal districts.
4. Sequential two-stage cultivation system using novel microalga consortia for treatment of municipal wastewater and simultaneous biomass production: Sustainable environmental management
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 366, August 2024, 121711
Abstract
Monoculture-based microalgae cultivation systems to treat wastewater are well-reported. Despite that, this method has some limitations in terms of nutrient removal potential, environment adaptation, and low biomass productivity. Conversely, microalgae co-cultivation and a two-stage sequential cultivation system (TSSCS) recently emerged as a promising approach to improve the treatment process and biomass productivity through better adaptation to the environment. However, no outdoor large-scale experiments were reported using this approach which hinders the viability of the process.
Thus, in the present study, a sequential two-stage large-scale outdoor novel microalgae consortia experiment was developed. In first stage consortia-assisted sequential cultivation, two ratios of Tetraselmis indica (TS) and one ratio of Picochlorum sp. (PC) (2 TS:1 PC) were cultivated in a 1000-L pond containing 75%-municipal wastewater (MWW) + 25%-ASN-III, while in the second stage, 2 PC:1 TS was cultivated in two different ponds, and each containing 375-L 2 TS:1 PC-treated water + 375-L ASN-III. Outdoor parameters and nutrient removal efficiency (NRE), biomass, and biomolecule productivity such as lipid, photosynthetic pigments, astaxanthin, and β-carotene were quantified, and cost analysis was performed. At the end of the first and second stages, 2 TS:1 PC and 2 PC:1 TS showed maximum NRE of COD (68.71 and 86.40%), TN (66.98 and 94.73%), and TP (82.70 and 94.36%), respectively. Moreover, 2 TS:1 PC and 2 PC:1 TS Pond 1 and 2 produced maximum dry biomass production; 2.41 and ∼ 2.54 g/L contained lipid content; 36.89 and 34.90% that have 86.50 and 55.79% FAME content respectively. Similarly, 2 TS:1 PC and 2 PC:1 TS biomass exhibited valuable pigments production of astaxanthin i.e., 0.56 and 0.35 mg/g, and β-carotene; 4.65 and 2.82 mg/g, respectively. The cost analysis suggested that only microalgal-based MWW treatment was unfeasible, while valorization of produced biomass into co-products could offset the operation costs and could allow the option for the microalgal-based sustainable approach for the treatment of MWW and recovery of valuable resources.
5. Applying the total carbon–black carbon approach method to investigate the characteristics of primary and secondary carbonaceous aerosols in ambient PM2.5 in northern Taiwan
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 936, 1 August 2024, 173476
Abstract
Ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) comprises a diverse array of carbonaceous species, and the impact of carbonaceous aerosols (CA) extends to both long-term and short-term effects on human health and the environment. Understanding the distinctive composition of CA is crucial for gaining insights into the origins of airborne particulate matter. Due to their diverse physicochemical properties and intricate heterogeneous reactions, CA often exhibits temporal and spatial variations. Ground-based and highly time-resolved apportionment methods play a vital role in discerning CA emissions. This study utilized high-time resolution data of total carbon (TC) and black carbon (BC) for CA apportionment in northern Taiwan. The advanced numerical model (TC-BC(λ)), coupled with continuous measurement data, facilitated CA allocation based on optical absorption characteristics, organic or elemental carbon composition, and the distinction between primary and secondary origins. Primary carbonaceous aerosols dominated the monitoring site, accounting for 67.5 % compared to the 32.5 % contribution from secondary forms of CA.
The summer season exhibited a maximum increase in secondary organic aerosols (SOA) at 41.5 %. Diurnal variations for primary emissions, such as BCc and primary organic aerosols (POA), showed marked peaks for BCff and POAnon-abs during morning rush hours. In contrast, BCbb and POABrC displayed bimodal peaks with increased concentrations during evening hours. Conversely, SOA exhibited significantly different diurnal trends, with SOABrC peaking late at night due to aqueous phased reactions and a noontime peak of SOAnon-abs observed due to photo-oxidation processes. Furthermore, the study employed backward trajectory analysis and concentration-weighted trajectories (CWTs) to examine the long-range transport of CA, identifying potential sources, origins, and transport patterns of CA components to the receptor site in Taiwan during different seasons.
6. Urban forest species selection for improvement of ecological benefits in Polish cities – The actual and forecast potential
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 366, August 2024, 121732
Abstract
Trees in cities perform important environmental functions: they produce oxygen, filter pollutants, provide habitat for wildlife, mitigate stormwater runoff, and reduce the effects of climate change, especially in terms of lowering temperatures and converting carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into stored carbon. Generally, to increase the environmental benefits of urban forests, the number of trees is increased, directly influencing the canopy coverage. However, little is known about potential of modifying the species composition of urban tree communities in order to increase ecological benefits. Planting and managing trees to increase canopy is particularly challenging in city centres, where the dense, often historic infrastructure of buildings and roads do not allow for a significant increase in greenspace. Estimations of canopy cover obtained through i-Tree Canopy analysis unveiled significant potential to increase canopy cover in historical urban areas in Polish cities from 15-34% to 31–51%.
This study models the ecological benefits of urban forests in Polish cities, focusing on how different species compositions can enhance environmental functions such as carbon sequestration and pollution filtration. Two main scenarios were analyzed: one involving the addition of trees based on the most common species currently planted (“standard option” SO), and another incorporating changes to the species composition to enhance ecological benefits (“city specific option” SCO). Acer platanoides (14.5%) and Tilia cordata (11.45%) were the most frequently species of Polish cities. Betula pendula, Quercus robur, Robinia pseudoacacia, Fraxinus excelsior, Acer pseudoplatanus, Aesculus hippocastanum and Acer campestre were also common species in urban forest communities (up to 5%). The diverse range of tree species in Polish cities contributes significantly to the overall carbon sequestration potential. The results suggest that modifying species composition could significantly increase carbon sequestration rates by 47.8%–114% annually, with the city specific option (SCO) being the most effective in enhancing carbon sequestration potential. This highlights the importance of strategic species selection in urban forestry practices to maximize environmental benefits and mitigate climate change effects.
7. Biochar and peat amendments affect nitrogen retention, microbial capacity and nitrogen cycling microbial communities in a metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated urban soil
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 936, 1 August 2024, 173454
Abstract
Soil contaminants may restrict soil functions. A promising soil remediation method is amendment with biochar, which has the potential to both adsorb contaminants and improve soil health. However, effects of biochar amendment on soil-plant nitrogen (N) dynamics and N cycling microbial guilds in contaminated soils are still poorly understood. Here, a metal- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) contaminated soil was amended with either biochar (0, 3, 6 % w/w) and/or peat (0, 1.5, 3 % w/w) in a full-factorial design and sown with perennial ryegrass in an outdoor field trial. After three months, N and the stable isotopic ratio δ15N was measured in soil, roots and leaves, along with microbial responses. Aboveground grass biomass decreased by 30 % and leaf N content by 20 % with biochar, while peat alone had no effect.
Peat in particular, but also biochar, stimulated the abundance of microorganisms (measured as 16S rRNA gene copy number) and basal respiration. Microbial substrate utilization (MicroResp™) was altered differentially, as peat increased respiration of all carbon sources, while for biochar, respiration of carboxylic acids increased, sugars decreased, and was unaffected for amino acids. Biochar increased the abundance of ammonia oxidizing archaea, while peat stimulated ammonia oxidizing bacteria, Nitrobacter-type nitrite oxidizers and comB-type complete ammonia oxidizers. Biochar and peat also increased nitrous oxide reducing communities (nosZI and nosZII), while peat alone or combined with biochar also increased abundance of nirK-type denitrifiers. However, biochar and peat lowered leaf δ15N by 2–4 ‰, indicating that processes causing gaseous N losses, like denitrification and ammonia volatilization, were reduced compared to the untreated contaminated soil, probably an effect of biotic N immobilization.
Overall, this study shows that in addition to contaminant stabilization, amendment with biochar and peat can increase N retention while improving microbial capacity to perform important soil functions.
8. Modelling future land use land cover changes and their impacts on urban heat island intensity in Guangzhou, China
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 366, August 2024, 121787
Abstract
During rapid urbanization in developing countries, changes in land use and land cover (LULC) can significantly alter urban land surface temperatures (LST), exacerbating the urban heat island (UHI) effect and degrading the outdoor environment. In this study, taking Guangzhou, China, as an example, we used Landsat series satellite data from 1992 to 2022, classified the LULC of the study area by the Support Vector Machine (SVM) method, estimated the LST of the area by the mono-window algorithm, and classified the LST of the study area into five UHI intensity classes based on the normalized values of the LST, and explored the influence of the LULC on the distribution of the UHI intensity.
The CA-ANN (cellular automata-artificial neural network) model in QGIS software was employed to forecast the distribution of LULC and UHI intensity in Guangzhou for 2032. The findings reveal a strong correlation between UHI intensity and LULC, with water bodies and vegetation primarily exhibiting low and sub-low temperatures, while urban areas exhibit sub-high and high temperatures. The prediction results show that, according to the current development trend, compared with 1992, the water body and vegetation cover in 2032 will decrease by 46.97% and 34.24%, the building land will increase by 263.71%, and the sub-high and high temperature areas will increase by 127.76% and 375.92%. By analysing the spatial and temporal changes in LULC and its relationship with the distribution of UHI intensity during urbanization, this study assists government administrations and urban planners in devising sensible urban development strategies and implementing effective measures to plan LULC rationally. This approach aims to mitigate the impacts of the urban heat island and foster sustainable urbanization.
9. Characteristics and effects of global sloping land urbanization from 2000 to 2020
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 937, 10 August 2024, 173348
Abstract
Cities usually expand on flat land. However, in recent decades, the increasing scarcity of available flat land has compelled many cities to expand to sloping land (sloping land urbanization, SLU), and the understanding for global SLU is still unclear. This study, based on the currently available high-precision global Digital Elevation Model (FABDEM) and global land cover dataset (GlobeLand30), investigated the characteristics and impacts of SLU in 26,402 urban residential areas worldwide from 2000 to 2020. Results show that the total area of SLU globally is 16,383 km2, accounting for 9.54 % of the overall urban expansion.
This phenomenon is widespread globally and relatively concentrated in a few countries, with 42.78 %, 24.35 %, and 21.83 % of the area coming from cultivated land, forest, and grassland respectively. Global SLU has accommodated 34.78 million urban population, and indirectly protected 8922 km2 of flat cultivated land, while causing a net loss of 4373 km2 of green ecological land. Deliberately balancing the dual effects of SLU is crucial for advancing sustainable global urbanization.
10. Enhanced resilience in urban stormwater management through model predictive control and optimal layout schemes under extreme rainfall events
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 366, August 2024, 121767
Abstract
Optimizing the layout of urban stormwater management systems is an effective method for mitigating the risk of urban flooding under extreme storms. However, traditional approaches that consider only economic costs or annual runoff control rates cannot dynamically respond to the uncertainties of extreme weather, making it difficult to completely avoid large accumulations of water and flooding in a short period. This study proposes an integrated method combining system layout optimization and Model Predictive Control(MPC)to enhance the system’s resilience and effectiveness in flood control. An optimization framework was initially built to identify optimal system layouts, balancing annual average life cycle cost (AALCC) and resilience index.
The MPC was then applied to the optimal layout selected using the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) method, aiming to alleviate inundation cost-effectively. The adaptability of MPC to varying sets of control horizons and its efficacy in managing the hydrograph and flood dynamics of urban drainage system were examined. Conducted in Yubei, Chongqing, this study revealed patterns in optimal layout fronts among various extreme design rainfalls, showing that peak position rate and return period significantly influence system resilience. The contribution of MPC to the optimal system layout was particularly notable, resulting in improved instantaneous and overall flood mitigation. The application of MPC increased the resilience index by an average of 0.0485 and offered cost savings of 0.0514 million yuan in AALCC. Besides, our findings highlighted the importance of selecting an optimal set of control horizons for MPC, which could reduce maximum flood depth from 0.43m to 0.19m and decrease conduit peak flow by up to 14% at a flood-prone downstream location.
11. Spatial heterogeneity of the effects of river network patterns on water quality in highly urbanized city
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 937, 10 August 2024, 173549
Abstract
River water quality deterioration is a serious problem in urban water environments. River network patterns affect water quality by influencing the flow, mixing, and other processes of water bodies. However, the effects of urban river network patterns on water quality remain poorly understood, thereby hindering the urban planning and management decision-making process. In this study, the geographically weighted regression (GWR) model was used to explore the spatial heterogeneity of the relationship between river network pattern and water quality.
The results showed that the river network has a complex structure, high connectivity, and relatively even distribution and morphology. Important river structure indicators affecting water quality included the water surface ratio (Wp) and multifractal features (∆α, ∆f) while important river connectivity indicators included circuitry (α) and network connectivity (γ). River structure has a more complex effect on water quality than connectivity. This study recommends that the Wp should be increased in agricultural areas and appropriately reduced in urban built-up areas, and the number of river segments and nodes should be controlled within a rational configuration. Our study provides key insights for evaluating and optimizing the river network patterns to improve water quality of urban rivers. In the future, the land use intensity, hydrological processes, and human activities should be coupled with the river network pattern to deepen our understanding of urban river environment.
12. Climate change impacts on magnitude and frequency of urban floods under scenario and model uncertainties
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 366, August 2024, 121679
Abstract
Many studies have confirmed that climate change leads to frequent urban flooding, which can lead to significant socioeconomic repercussions. However, most existing studies have not evaluated the impacts of climate change on urban flood from both event-scale and annual-scale dimensions. In addition, there are only few studies that simultaneously consider scenario and model uncertainties of climate change, and combine flood risk assessment and uncertainty analysis results to provide practical suggestions for urban drainage system management.
This study uses the statistical downscaling method to calculate the design rainfall under ten rainfall return periods of four climate models and three climate change scenarios in 2040s, 2060s, and 2080s in various prefecture-level cities in China. The four climate models are HadGEM2- ES, MPI-ESM-MR, NorESM1-M and FGOALS-g2 models and the three climate change scenarios are constructed by different representative concentration pathways (RCP), namely RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5. On this basis, relying on the generated drainage systems using geographical information and other data, event-scale and annual-scale precipitation are combined to calculate the change ratio of annual flood volume expectation in prefecture-level cities in each future year compared with the current situation. Furthermore, the study evaluates scenario and model uncertainties of climate change, and then comprehensively integrates the flood risk and its uncertainties to provides suggestions for urban drainage system management.
13. The synergistic effect of high temperature and relative humidity on non-accidental deaths at different urbanization levels
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 940, 25 August 2024, 173612
Abstract
Numerous studies have examined the impact of temperature on mortality, yet research on the combined effect of temperature and humidity on non-accidental deaths remains limited. This study investigates the synergistic impact of high temperature and humidity on non-accidental deaths in China, assessing the influence of urban development and urbanization level. Utilizing the distributed lag nonlinear model (DLNM) of quasi-Poisson regression, we analyzed the relationship between Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) and non-accidental deaths in 30 Chinese cities from 2010 to 2016, including Guangzhou during 2012–2016. We stratified temperature and humidity across these cities to evaluate the influence of varying humidity levels on deaths under high temperatures.
Then, we graded the duration of heat and humidity in these cities to assess the impact of deaths with different durations. Additionally, the cities were categorized based on gross domestic product (GDP), and a vulnerability index was calculated to examine the impact of urban development and urbanization level on non-accidental deaths. Our findings reveal a pronounced synergistic effect of high temperature and humidity on non-accidental deaths, particularly at elevated humidity levels. The synergies of high temperature and humidity are extremely complex. Moreover, the longer the duration of high temperature and humidity, the higher the risk of non-accidental death. Furthermore, areas with higher urbanization exhibited lower relative risks (RR) associated with the synergistic effects of heat and humidity. Consequently, it is imperative to focus on damp-heat related mortality among vulnerable populations in less developed regions.
14. Spatial patterns and influencing factors of takeaway consumption in 56 cities in China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 465, 1 August 2024, 142712
Abstract
With the development of the digital economy, the takeaway industry is expanding rapidly. To realize the high-quality development of the takeaway sector, it is necessary to understand the spatial differentiation characteristics of takeaway consumption in Chinese cities and its influencing factors. To this end, we quantitatively studied the spatial distribution of takeaway consumption in 56 cities. We used the number of takeaway orders (copies/person) and the per capita takeaway consumption amount (RMB/person) in major Chinese cities in 2019 to characterize takeaway consumption in China. We investigated the driving mechanisms and factors affecting takeaway consumption amounts per capita and order per capita in China.
The results show that takeaway consumption amounts per capita and order per capita is higher in East China than in North and Central China. The tertiary industry population ratio is crucial to takeaway consumption amounts per capita and order per capita in major Chinese cities. Amounts and orders increase as the tertiary industry population ratio rises. Factors affecting takeaway consumption amounts per capita and order per capita in Chinese cities of different population sizes vary. The working-age population ratio heavily influences the takeaway consumption amounts per capita and orders per capita in megacities. Additionally, internet penetration and average annual temperature play a significant role in takeaway consumption amounts per capita and orders per capita in megalopolis. In big cities Ⅰ, the road capacity per capita and GDP per capita are the main factors affecting takeaway consumption amounts per capita and orders per capita.
The tertiary industry population ratio is the core factor that determines takeaway consumption amounts per capita and orders per capita in big cities Ⅱ. The interaction between natural and socio-economic factors dramatically increases the impact of takeaway consumption amounts per capita and order per capita in Chinese cities. In conclusion, this study provides a macro-level insight into the spatial characteristics and development factors of takeaway consumption in major Chinese cities. This knowledge is crucial for promoting the takeaway economy’s sustainable development and realizing the takeaway industry’s green transformation.
15. Associations between atmospheric PM2.5 exposure and carcinogenic health risks: Surveillance data from the year of lowest recorded levels in Beijing, China
Environmental Pollution, Volume 355, 15 August 2024, 124176
Abstract
Scant research has pinpointed the year of minimum PM2.5 concentration through extensive, uninterrupted monitoring, nor has it thoroughly assessed carcinogenic risks associated with analyzing numerous components during this nadir in Beijing. This study endeavored to delineate the atmospheric PM2.5 pollution in Beijing from 2015 to 2022 and to undertake comprehensive evaluation of carcinogenic risks associated with the composition of atmospheric PM2.5 during the year exhibiting the lowest concentration. PM2.5 concentrations were monitored gradually in 9 districts of Beijing for 7 consecutive days per month from 2015 to 2022, and 32 kinds of PM2.5 components collected in the lowest PM2.5 concentration year were analyzed. This comprehensive dataset served as the basis for carcinogenic risk assessment using Monte Carlo simulation.
And we applied the Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) method to identity the sources of atmospheric PM2.5. Furthermore, we integrated this source appointment model with risk assessment model to discern the origins of these risks. The findings revealed that the annual average PM2.5 concentration in 2022 stood at 43.1 μg/m3, marking the lowest level recorded. The mean carcinogenic risks of atmospheric PM2.5 exposure calculated at 6.30E-6 (empirical 95% CI 1.09E-6 to 2.25E-5) in 2022. The PMF model suggested that secondary sources (35.4%), coal combustion (25.6%), resuspended dust (15.1%), biomass combustion (14.1%), vehicle emissions (7.1%), industrial emissions (2.0%) and others (0.7%) were the main sources of atmospheric PM2.5 in Beijing. The mixed model revealed that coal combustion (2.41E-6), vehicle emissions (1.90E-6) and industrial emissions (1.32E-6) were the main sources of carcinogenic risks with caution. Despite a continual decrease in atmospheric PM2.5 concentration in recent years, the lowest concentration levels still pose non-negligible carcinogenic risks. Notably, the carcinogenic risks associated with metals and metalloids exceeded that of PAHs. And the distribution of risk sources did not align proportionally with the distribution of PM2.5 mass concentration.
16. Assessing risk of metro microenvironmental health vulnerability from the coupling perspective: A case of Nanjing, China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 466, 10 August 2024, 142861
Abstract
Metro, as a convenient transportation, has many potential environmental risks during operation that pose a great threat to users, resulting in metro microenvironmental health vulnerability (MMHV). While prior research has focused on metro construction and safety management, some investigations have also addressed isolated metro microenvironment factors, such as air quality and noise, ignoring the underlying causes of health risks. Therefore, this research aims to reveal driving factors contributing to MMHV and assess the risk of MMHV from the coupling perspective. 14 Driving factors related to personnel, facility, environment, and management were firstly identified, along with their coupling relationships.
Then, a risk coupling simulation model of the identified driving factors has been devised, which integrates a cloud theory-based coupling degree model framework and system dynamics principles to represent the interconnected risks posed by these factors. Finally, the constructed model is applied practically to discern the developmental trajectory of coupled risks emanating from the driving factors influencing MMHV. And the key factors at different periods were determined by adjusting coupling coefficients, so as to propose targeted strategies. Findings in this research offer valuable guidance for the implementation of diversified and precisely tailored measures to address MMHV at various stages of metro operation. This, in turn, contributes to the mitigation of health risks and ensures the sustained and healthy operation and management of metro.
INDUSTRIAL AREA ENVIRONMENT / MÔI TRƯỜNG KHU CÔNG NGHIỆP
1. Occurrence and combined exposure of phthalate esters in urban soil, surface dust, atmospheric dustfall, and commercial food in the semi-arid industrial city of Lanzhou, Northwest China
Environmental Pollution, Volume 354, 1 August 2024, 124170
Abstract
A total of 138 samples including urban soil, surface dust, atmospheric dustfall, and commercial food were collected from the semi-arid industrial city of Lanzhou in Northwest China, and 22 phthalate esters (PAEs) were analyzed in these samples by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the pollution characteristics, potential sources, and combined exposure risks of PAEs. The results showed that the total concentration of 22 PAEs (Ʃ22PAEs) presented surface dust (4.94 × 104 ng/g) ≫ dustfall (1.56 × 104 ng/g) ≫ food (2.14 × 103 ng/g) ≫ urban soil (533 ng/g). Di-n-butyl phthalate (DNBP), di-isobutyl phthalate, di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), and di-isononyl phthalate/di-isodecyl phthalate were predominant in the environmental media and commercial food, being controlled by priority (52.1%–65.5%) and non-priority (62.1%) PAEs, respectively. Elevated Ʃ22PAEs in the urban soil and surface dust was found in the west, middle, and east of Lanzhou.
Principal component analysis indicated that PAEs the urban soil and surface dust were related with the emissions of products containing PAEs, atmosphere depositions, and traffic and industrial emissions. PAEs in the foods were associated with the growth and processing environment. The health risk assessment of United States Environmental Protection Agency based on the Chinese population exposure parameters indicated that the total exposure dose of 22 PAEs was from 0.111 to 0.226 mg/kg/day, which were above the reference dose (0.02 mg/kg/day) and tolerable daily intake (TDI, 0.05 mg/kg/day) for DEHP (0.0333–0.0631 mg/kg/day), and TDI (0.01 mg/kg/day) for DNBP (0.0213–0.0405 mg/kg/day), implying that the exposure of PAEs via multi-media should not be ignored; the total non-carcinogenic risk of six priority PAEs was below 1 for the three environmental media (1.21 × 10−5–2.90 × 10−3), while close to 1 for food (4.74 × 10−1–8.76 × 10−1), suggesting a potential non-carcinogenic risk of human exposure to PAEs in food; the total carcinogenic risk of BBP and DEHP was below 1 × 10−6 for the three environmental media (9.13 × 10−10–5.72 × 10−7), while above 1 × 10−4 for DEHP in food (1.02 × 10−4), suggesting a significantly carcinogenic risk of human exposure to DEHP in food. The current research results can provide certain supports for pollution and risk prevention of PAEs.
2. Synergetic effect evaluation of pollution and carbon emissions in an industrial park: An environmental impact perspective
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 467, 15 August 2024, 142891
Abstract
How to achieve synergistic control of pollution and carbon emissions has become a global concern. This article focuses on an industrial park and aims to evaluate the synergistic effect of pollution and carbon emissions from an environmental impact perspective. We propose a synergistic effect evaluation method based on life cycle assessment (LCA-SE method). The synergistic effect index (Els) indicates that the industrial park exhibits a strong synergistic effect in reducing pollution and carbon emissions. Based on our findings, we draw the following conclusions: First, carbon emissions should be given priority in emissions control.
Second, photovoltaic power generation and energy conservation measures can effectively achieve synergistic efficiency in reducing pollution and carbon emissions. Third, when considering synergistic control of pollution and carbon emissions, priority should be given to pollutant reduction measures that can simultaneously reduce energy consumption during the process. This study presents a novel approach, the LCA-SE method, to assessing the synergistic impact of pollution and carbon emissions, offering valuable insights into the coordinated management of pollution and carbon emissions in China.
3. Prediction of carbon emissions in China’s construction industry using an improved grey prediction model
Science of The Total Environment, Volume 938, 15 August 2024, 173351
Abstract
As a significant source of global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, the construction industry garners widespread attention due to its high carbon emissions. Anticipating its development trends is crucial for energy conservation and emission reduction. In this paper, we utilize the carbon emission data from China’s national and provincial construction sectors from 2012 to 2021, employ the grey prediction model optimized by the particle swarm optimization algorithm, coupled with a metabolic algorithm, to forecast the carbon emissions of the construction industry across China and its provinces.
The results demonstrate that: (1) The dynamic grey prediction model combined with the metabolism algorithm has a better prediction effect than the classical model, and the relative error is reduced from 5.103 % to 0.874 %. (2) The carbon emissions of China’s construction industry will continue to rise in the next decade, but the growth rate will decrease, and the proportion of indirect carbon emissions continues to increase. (3) There is a marked regional disparity in carbon emissions, with the eastern region exhibiting higher emission levels yet slower growth. In contrast, the western region has lower emission levels but experiences faster growth. These studies provide valuable insights for both the existing approaches to energy conservation and emission reduction, as well as for future policy improvements.
4. Carbon–water–energy footprint impacts of dyed cotton fabric production in China
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 467, 15 August 2024, 142898
Abstract
The textile industry, associated with substantial resource consumption, has posed crucial environmental challenges, mainly in climate change, energy, and water crisis. Considering that cotton is the most manufactured natural fiber and that textile dyeing plays an indispensable role in serving people’s demand for fashion and aesthetics, this study conducted an integrated impact-oriented carbon–water–energy (CWE) footprint analysis of dyed cotton fabric production in China from a cradle-to-gate perspective. Results showed that the carbon, energy, and freshwater ecotoxicity footprints of dyeing 1 ton of pure cotton fabrics were 15627.20 kg CO2 eq, 3405.30 kg oil eq, and 2.01 × 105 PAF·m3·d, respectively. Fiber production, chemical production, and direct emissions were identified as the major contributors to CWE footprints. Cotton straw mulching, advanced dyeing technology, and national power structure optimization were explored to foster sustainable optimization of the cotton-made textile industry.
At the conventional wet-processing stage, the dyeing phase had the greatest contribution (56.3%–85.6%) to the environmental impacts from chemicals, followed by pretreatment with a 13.8%–28.3% share. Nonaqueous dyeing routes reduced carbon footprint by 49.1% and water scarcity by 75% compared with water-based dyeing processes, with noticeable increases in noncarcinogen and carcinogen categories. Comprehensive wastewater discharge regulations should be further developed, and the scientific layout between regions along the supply chain from the upstream link to dyeing areas should be strengthened to effectively manage environmental pressures in the textile dyeing industry.
5. Global nanocatalysts strategic research report 2024: Market to reach $4.1 bn by 2030 – Nanocatalysts emerge as eye-grabbing option for hydrotreating in petroleum industry
Focus on Catalysts, Volume 2024, Issue 8, August 2024, Page 2
Abstract
The global market for nanocatalysts is estimated at $2.5 bn in 2023 and is projected to reach $4.1 bn by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. The global nanocatalysts market is on the brink of rapid growth, driven by recent advancements in nano-catalysis and its expanding range of applications. Market growth: Understand the significant growth trajectory of the refinery & petrochemicals application segment, which is expected to reach $1.7 bn by 2030 with a CAGR of 6.7%. The environment application segment is also set to grow at 7.5% CAGR over the next 8 years. Regional analysis: Gain insights into the US market, estimated at $631.9 M in 2023, and China, forecasted to grow at an impressive 7.4% CAGR to reach $547.3 M by 2030. Discover growth trends in other key regions, including Japan, Canada, Germany, and the Asia-Pacific. Select competitors (total 55 featured): BASF SE, Dow Inc, Evonik Industries AG, Johnson Matthey Plc, Kronos Worldwide Inc, Nexceris, PQ Corporation, TitanPE Technologies Inc, Umicore NV, Venator Materials PLC, W. R. Grace & Co, and Zeolyst International. A table shows the report attribute. A graph shows the nanocatalysts market in 2023 and 2030.
6. The impact of China’s carbon emissions trading policy on corporate investment expenditures: Evidence from carbon-intensive industries
Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 366, August 2024, 121743
Abstract
The carbon emissions trading (CET) policy internalises the cost of carbon emission reductions borne by companies, which will affect the companies’ investment and management decisions. From a micro perspective, this paper analyzes the impact on company investment expenditure and its transmission mechanism by implementing the CET policy. Based on panel data of China’s A-share listed companies from eight carbon-intensive industries spanning 2010 to 2020, the time-varying difference-in-difference model and its extended model are used to evaluate the impact of the policy in the pilot areas. The results show that: first, based on the cost effect and legality theories, CET policy can reduce the investment expenditure of the companies by 71.95%. Second, CET policy reduces corporate investment expenditures by increasing corporate debt financing costs.
When debt financing costs increase by 120.25%, the investment expenditures will reduce by 2.56% indirectly while the intermediary effect of equity financing costs is not significant. Finally, with the implementation of CET policy, the inhibitory effect on corporate investment expenditures has gradually increased. CET policy has a more significant inhibitory effect on investment expenditures of nonstate-owned companies and small-scale companies. The results have passed the robustness test and provide evidence for the policy-maker to balance microeconomic entity development and carbon reduction, and for companies to make optimization investment and financing decisions in response to policy shocks effectively.
7. Assessment of the green hydrogen value chain in cases of the local industry in Chile applying an optimization model
Energy, Volume 300, 1 August 2024, 131630
Abstract
This study assessed the feasibility of integrating a green hydrogen value chain into the local industry, examining two case studies by comparing four scenarios. The optimization focused on generating electricity from stationary renewable sources, such as solar or through Power Purchase Agreements, to produce sufficient hydrogen in electrolyzers. Current demand profiles, renewable participation targets, electricity supply sources, levelized costs of energy and hydrogen, and technology options were considered.
The most cost-effective scenario showed a levelized cost of energy of 0.032 and 0.05 US$/kWh and a hydrogen cost below 1.0 US$/kgH2 for cases 1 and 2, respectively. A sensitivity analysis highlighted the critical influence of fuel cell technology on cost modification, underscoring the importance of focusing cost reduction strategies on these technologies to enhance the economic viability of the green hydrogen value chain. Specifically, a high sensitivity towards reducing the levelized costs of energy and hydrogen in the port sector with adjustments in fuel cell technology costs was identified, indicating the need for specific policies and supports to facilitate their adoption.
8. Probabilistic safety and reliability studies toward licensing and deploying HTGR technology in the Polish chemical industry
Nuclear Engineering and Design, Volume 424, 1 August 2024, 113244
Abstract
The pivotal aspects of the Probabilistic Safety Assessment (PSA) and reliability studies for the foreseen HTGR-based nuclear-chemical (Nuc-Chem) facilities are discussed. The traditional PSA methodology has been extended to include the mutual dependence of nuclear and chemical systems of the hybrid Nuc-Chem installations, where HTGR serves as a heat source for various chemical processes.
The Dynamic Bayesian Network (DBN) approach has been utilized for modeling time sequences of failures, including interactions between nuclear and non-nuclear systems, as well as external hazards. The Global Variance Method (GVM), based on the Sobol indices, has been proposed for uncertainty and sensitivity studies concerning numerous sources of variability in a consistent manner. The paper presents the outcomes and achievements from research oriented toward licensing and deploying High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGR) within the Polish chemical industry. The general framework developed in this work for PSA of the hybrid Nuc-Chem facilities can be applied to support the licensing process and safe operation of the Polish chemical plants to be equipped with HTGRs.
9. Recent advances on energy management and control of direct current microgrid for smart cities and industry: A Survey
Applied Energy, Volume 368, 15 August 2024, 123501
Abstract
Recently, the intent to use microgrid (MG) technology for urban, residential, and industrial applications has significantly increased. Thanks to the integration of shared storage technologies, these power systems allow for higher penetration of distributed renewable generation (DGs) and better mitigation of imbalances between demand and generation. This responds to social and environmental requirements in terms of decarbonizing energy and also contributes to strengthening smart cities. DC (Direct Current) microgrids offer several advantages compared to AC (Alternating Current) type microgrids, like superior efficiency, better control, stability, compatibility with the DC nature of renewables and storage sources, and the absence of reactive and synchronization problems.
However, before fully exploiting the potential of microgrids in renewable-powered smart grids, it is necessary to conduct further research and discussion on critical technical and socio-economic challenges. This paper presents a review of the existing state-of-the-art research in DC microgrid development, relevant challenges related to security, communication, power quality, and operation, as well as the appropriate control and energy management strategies to handle them. As control and energy management strategies considerably impact other performance indicators such as operating cost, emissions, and power system safety, this paper offers a perspective on the potential improvement of such management solutions.
10. ESG performance and green innovation in new energy enterprises: Does institutional environment matter?
Research in International Business and Finance, Volume 71, August 2024, 102495
Abstract
As the demand for sustainable production grows across Chinese society, heightened attention is being paid to new energy enterprises with superior green innovation capabilities in the current environment. Given the considerable importance of environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance to business operations, we use a sample of 192 Chinese A-share listed new energy enterprises from 2009 to 2022 to investigate the impact of ESG performance on green innovation from the institutional environment perspective.
The empirical findings indicate that ESG performance and the institutional environment significantly contribute to facilitating new energy enterprises’ green innovation and the institutional environment can strengthen the promoting effect of ESG performance on green innovation. In addition, ESG performance and the institutional environment can have a significant influence on promoting green innovation in non-state-owned enterprises and new energy enterprises of all sizes, while the moderating effect of the institutional environment only has a positive influence on non-state-owned and large new energy enterprises. Finally, comparing the discrepancy between new energy enterprises’ substantive and strategic green innovation, ESG performance, institutional environment and its optimisation effect tend towards the former.
11. Corporate misconduct and innovation: Evidence from the pharmaceutical industry
Research in International Business and Finance, Volume 71, August 2024, 102490
Abstract
We examine the relationship between corporate misconduct and pharmaceutical firm innovation and performance. Pharmaceutical firms obtain significantly fewer new product approvals by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) following corporate regulatory violations, lawsuits, and Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulatory enforcement actions. We also examine the potential reasons why innovative capacity is reduced for culpable firms.
Following instances of misconduct, pharmaceutical firms are 50 percent less likely to engage in business expansions, engage in significantly fewer new strategic alliances and partnerships, and are awarded fewer government R&D grants. We attribute these results to the reputational loss associated with public knowledge of corporate misconduct. In support of this hypothesis, we find pharmaceutical firms experience negative cumulative abnormal stock returns (CARs) surrounding SEC enforcement announcements, and misconduct incidents increase the probability of analyst concerns. Overall, our results are consistent with the reputational loss associated with corporate misconduct being an important factor in future reductions in pharmaceutical firm innovative capacity.
12. Beyond the Clock: Revisiting Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs) for unusual work schedules in the South African
Mining Industry Safety Science, Volume 176, August 2024, 106542
Abstract
Workers are exposed to various stressors in their workplace and in many industries, exposure is prolonged due to unusual work schedules. Workers are exposed to various stressors in their workplace and in many industries, exposure is prolonged due to unusual work schedules. Unfortunately, current Occupational Exposure Limits (OELs) are derived from calculations based on a conventional work schedule of five consecutive, eight-hour days (40 h per week) and do not compensate for prolonged exposure and shortened recovery time.
Therefore, standard OELs must be adjusted to ensure worker protection. The aim of this paper was to review different mathematical models available in the literature to adjust OELs for unusual work schedules. Based on the advantages, disadvantages and practical feasibility of the different models, the Brief and Scala, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Québec models were selected to calculate reduction factors (RFs, i.e., adjustment factors) for three unusual work schedules encountered in the South African Mining Industry (SAMI). Subsequently, the calculated RFs were used to establish adjusted OELs (OELA) for 15 chemical substances of interest. The Brief and Scala model yielded the most conservative RFs for all work schedule examples. However, this model may overestimate the degree to which the OELs should be lowered. The OSHA and Québec models incorporate pharmacokinetic parameters (i.e., primary health effects) and generated more realistic RFs compared to the Brief and Scala model. Although pharmacokinetic-based models are more accurate from a toxicological viewpoint, the anatomical, physiological, biochemical, and physiochemical parameters required to apply these models are not available for many chemical substances and therefore the use of such pharmacokinetic-based models is not practically feasible in South Africa. Based on the findings of this study, the authors recommend using the OSHA or Québec models for OEL adjustments in the SAMI. OELs adjusted in this manner will provide an equivalent degree of worker protection during unusual work schedules compared to conventional work shifts.
13. Recent advances on energy management and control of direct current microgrid for smart cities and industry: A Survey
Applied Energy, Volume 368, 15 August 2024, 123501
Abstract
Recently, the intent to use microgrid (MG) technology for urban, residential, and industrial applications has significantly increased. Recently, the intent to use microgrid (MG) technology for urban, residential, and industrial applications has significantly increased. Thanks to the integration of shared storage technologies, these power systems allow for higher penetration of distributed renewable generation (DGs) and better mitigation of imbalances between demand and generation. This responds to social and environmental requirements in terms of decarbonizing energy and also contributes to strengthening smart cities.
DC (Direct Current) microgrids offer several advantages compared to AC (Alternating Current) type microgrids, like superior efficiency, better control, stability, compatibility with the DC nature of renewables and storage sources, and the absence of reactive and synchronization problems. However, before fully exploiting the potential of microgrids in renewable-powered smart grids, it is necessary to conduct further research and discussion on critical technical and socio-economic challenges. This paper presents a review of the existing state-of-the-art research in DC microgrid development, relevant challenges related to security, communication, power quality, and operation, as well as the appropriate control and energy management strategies to handle them. As control and energy management strategies considerably impact other performance indicators such as operating cost, emissions, and power system safety, this paper offers a perspective on the potential improvement of such management solutions.
14. Co-flotation of effluents from detergent and marble processing industries in Denver and dispersed air flotation systems
Chemosphere, Volume 362, August 2024, 142728
Abstract
Suspended solids in the marble processing wastewater (MPWW) have the potential to pollute receiving media. Suspended solids in the marble processing wastewater (MPWW) have the potential to pollute receiving media. Likewise, detergent production wastewater (DPWW) needs treatment prior to discharge as they include surfactants and others. Flotation and its modifications are common for separation purposes in various engineering solutions. To increase flotation performance by changing the surface tension some collector and frother chemicals, surfactants are utilized. Detergents are among important surfactants and they may act as both frother and collector in flotation.
Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of DPWW in co-flotation with MPWW. Two effluents were mixed at varying ratios and dispersed air (DISP) and Denver (DEN) flotation co-treatment were applied to the mixtures. Volume ratio, time and air flow rate on treatment performance were investigated. Turbidity, solids, COD, phosphate removals were achieved at varying levels when the flotation was applied to the mixture. The highest treatment performance was achieved at 90%MPWW-10%DPWW mixture. 10 min flotation time and 2 L min−1 air flow rate for the DEN system, and 20 min and 6 L min−1 for the DISP system were recommended. Under these conditions turbidity, SS, COD, phosphate and alkalinity residuals (and removal efficiencies) were 2400 NTU(82%), 1720 mg.L−1(89%), 313.6 mg.L−1(10%), 20 mg.L−1(20%) and 600 mg.L−1CaCO3(92%) in the DEN system, respectively. Whereas, in the DISP system, under the same conditions, final values of 1880 NTU(86%), 1540 mg.L−1(91%), 262 mg.L−1(17%), 21 mg.L−1(20%) and 470 mg.L−1(94%) were obtained, respectively. The highest SludgeSS concentration increased up to 19300 mg.L−1 in the 90%–10% mixture. In all samples, dewaterable sludge was obtained. By this study, co-flotation of these two effluents was recommended. Within SDGs, this approach will replace frother chemical usage. The process performance can further be enhanced via flotation modifications and technology can be developed as further study.
15. Selective pressure leads to an improved synthetic consortium fit for dye degradation
Chemosphere, Volume 361, August 2024, 142489
Abstract
Microorganisms have great potential for bioremediation as they have powerful enzymes and machineries that can transform xenobiotics. The use of a microbial consortium provides more advantages in application point of view than pure cultures due to cross-feeding, adaptations, functional redundancies, and positive interactions among the organisms. In this study, we screened about 107 isolates for their ability to degrade dyes in aerobic conditions and without additional carbon source. From our screening results, we finally limited our synthetic consortium to Gordonia and Rhodococcus isolates. The synthetic consortium was trained and optimized for azo dye degradation using sequential treatment of small aromatic compounds such as phenols that act as selective pressure agents. After four rounds of optimization with different aims for each round, the consortium was able to decolorize and degrade various dyes after 48 h (80%–100% for brilliant black bn, methyl orange, and chromotrop 2b; 50–70% for orange II and reactive orange 16; 15–30% for chlorazol black e, reactive red 120, and allura red ac).
Through rational approaches, we can show that treatment with phenolic compounds at micromolar dosages can significantly improve the degradation of bulky dyes and increase its substrate scope. Moreover, our selective pressure approach led to the production of various dye-degrading enzymes as azoreductase, laccase-like, and peroxidase-like activities were detected from the phenol-treated consortium. Evidence of degradation was also shown as metabolites arising from the degradation of methyl red and brilliant black bn were detected using HPLC and LC-MS analysis. Therefore, this study establishes the importance of rational and systematic screening and optimization of a consortium. Not only can this approach be applied to dye degradation, but this study also offers insights into how we can fully maximize microbial consortium activity for other applications, especially in biodegradation and biotransformation.
16. Relating the carbon sources to denitrifying community in full-scale wastewater treatment plants
Chemosphere, Volume 361, August 2024, 142329
Abstract
Carbon source is a key factor determining the denitrifying effectiveness and efficiency in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). Whereas, the relationships between diverse and distinct denitrifying communities and their favorable carbon sources in full-scale WWTPs were not well-understood. This study performed a systematic analysis of the relationships between the denitrifying community and carbon sources by using 15 organic compounds from four categories and activated sludge from 8 full-scale WWTPs. Results showed that, diverse denitrifying bacteria were detected with distinct relative abundances in 8 WWTPs, such as Haliangium (1.98–4.08%), Dechloromonas (2.00–3.01%), Thauera (0.16–1.06%), Zoogloea (0.09–0.43%), and Rhodoferax (0.002–0.104%). Overall, acetate resulted in the highest denitrifying activities (1.21–4.62 mg/L/h/gMLSS), followed by other organic acids (propionate, butyrate and lactate, etc.). Detectable dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) was observed for all 15 carbon sources.
Methanol and glycerol resulted in the highest DRNA. Acetate, butyrate, and lactate resulted in the lowest DNRA. Redundancy analysis and 16S cDNA amplicon sequencing suggested that carbon sources within the same category tended to correlate to similar denitrifiers. Methanol and ethanol were primarily correlated to Haliangium. Glycerol and amino acids (glutamate and aspartate) were correlated to Inhella and Sphaerotilus. Acetate, propionate, and butyrate were positively correlated to a wide range of denitrifiers, explaining the high efficiency of these carbon sources. Additionally, even within the same genus, different amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) performed distinctly in terms of carbon source preference and denitrifying capabilities. These findings are expected to benefit carbon source formulation and selection in WWTPs.
CHUYÊN TRANG QUẢN LÝ MÔI TRƯỜNG
Tạp chí Môi trường và Đô thị Việt Nam















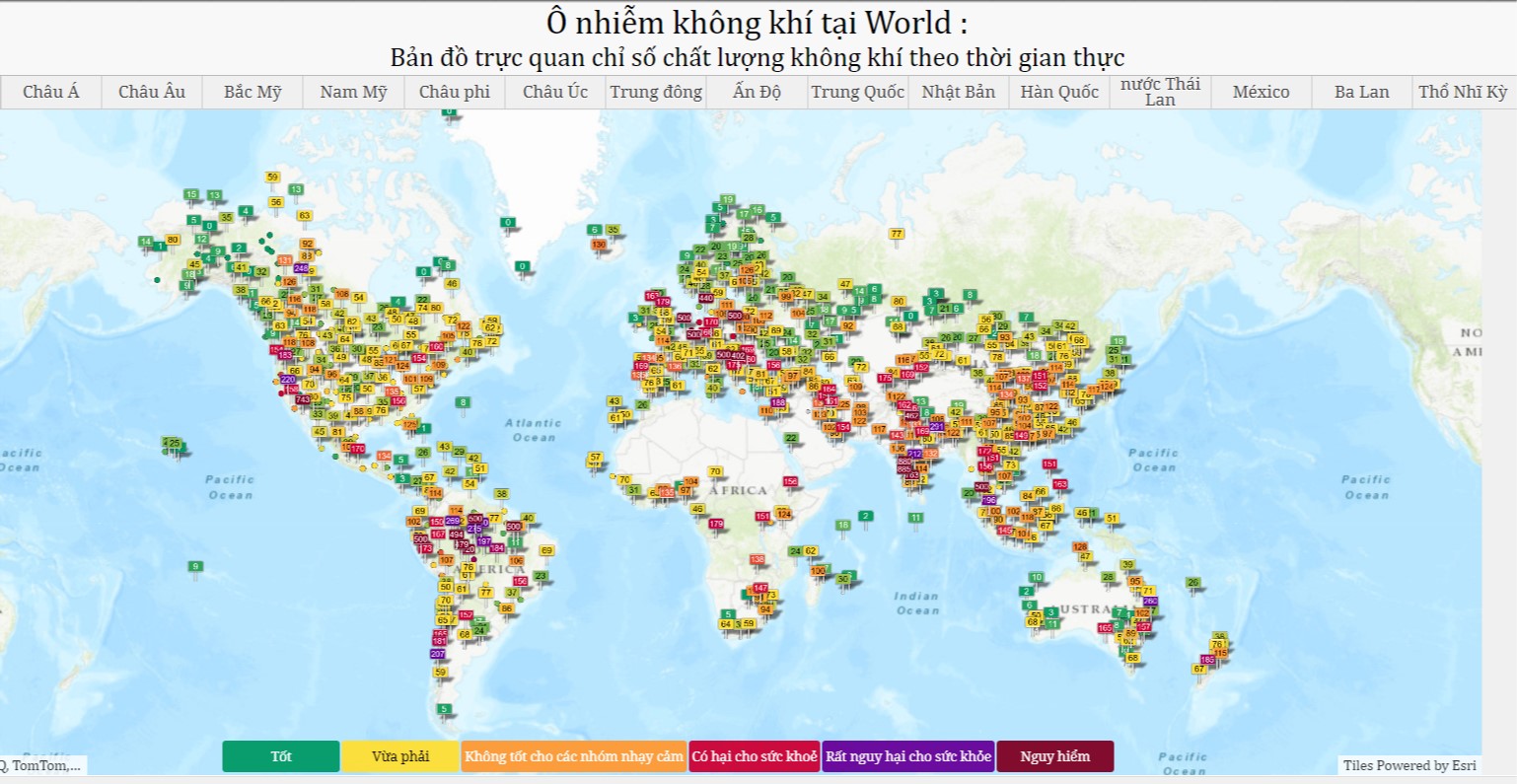 Bản đồ trực quan chỉ số chất lượng không khí trên thế giới ngày 17/9/2024. Nguồn: aqicn.org (
Bản đồ trực quan chỉ số chất lượng không khí trên thế giới ngày 17/9/2024. Nguồn: aqicn.org (








 Khách hàng trải nghiệm sử dụng Máy thay nhớt tự động 3R
Khách hàng trải nghiệm sử dụng Máy thay nhớt tự động 3R Các diễn giả trả lời báo chí
Các diễn giả trả lời báo chí Phương thức vận hành Máy 3R
Phương thức vận hành Máy 3R


